19 Major Bills Passed Including New Income Tax Act: When you hear the phrase “19 major bills passed including the new Income Tax Act while opposition stayed silent,” it sounds like the beginning of a political drama. But this actually happened in India’s Parliament during the Monsoon Session of August 2025. In just a few days, lawmakers rushed through 19 important bills, including the brand-new Income Tax Act, 2025. What made headlines wasn’t just the scale of the reforms, but the unusual silence of the opposition. No fiery debates, no long arguments, no back-and-forth. For citizens, businesses, and professionals alike, this was a moment that will shape India’s future for decades.
19 Major Bills Passed Including New Income Tax Act
The passage of 19 major bills—including the Income Tax Act, 2025—without debate is a landmark event in India’s political and economic history. On one hand, the country gets a simplified, digital-friendly tax system and reforms across multiple industries. On the other, the lack of debate raises concerns about democratic accountability. For taxpayers, businesses, and professionals, the message is clear: the rules of the game have changed. The challenge now is to adapt, stay informed, and make the most of this new framework.

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Bills Passed | 19 major bills, including Income Tax Act, 2025 |
| Lok Sabha Action | 12 bills passed without debate |
| Rajya Sabha Action | 15 bills approved amid uproar |
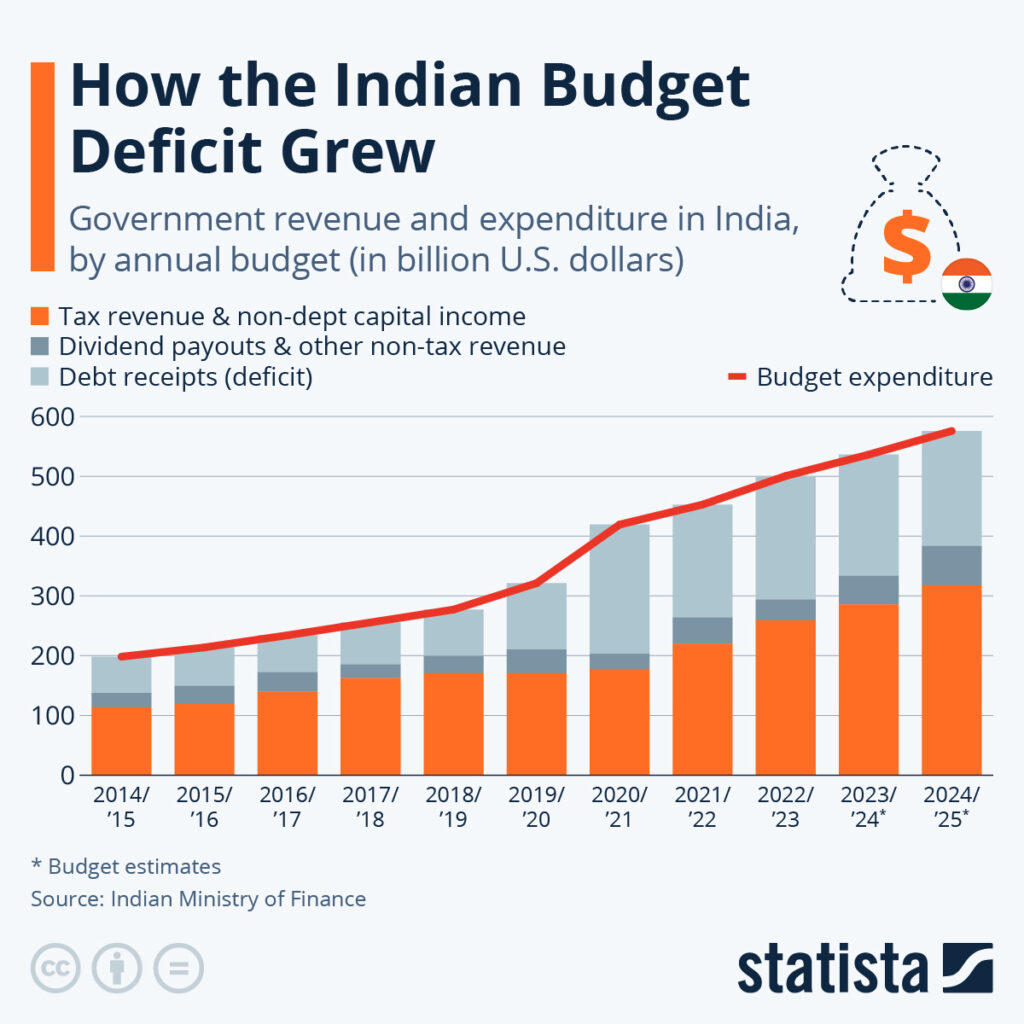
| Income Tax Act Details | Simplified: from 800+ sections to 536; ₹12 lakh exemption unchanged; enforcement from April 1, 2026 |
| Date of Passage | Lok Sabha: Aug 11, 2025; Rajya Sabha: Aug 12, 2025; Presidential Assent: Aug 21, 2025 |
| Other Bills | Sports governance, maritime reforms, online gaming regulation |
| Government’s View | Finance Minister shocked by “zero debate” |
| Official Reference | Government of India: Ministry of Finance |
What Exactly Happened in Parliament?
The Monsoon Session is usually a lively one. Think of it as a political arena—arguments, protests, walkouts, and marathon debates are the norm. But in August 2025, things were different.
In a move that surprised many, 19 bills were passed in record time. The most notable among them was the Income Tax Act, 2025, which finally replaced the Income Tax Act of 1961 after more than 60 years.
The unusual part wasn’t just the speed—it was the silence. The opposition benches were nearly mute, with most bills going through without debate. Even the Finance Minister, Nirmala Sitharaman, admitted later that she was “shocked” her flagship tax bill was passed without a single word of opposition.
Why India Needed 19 Major Bills Passed Including New Income Tax Act?
To understand the importance of this change, let’s rewind a little.
The Income Tax Act of 1961 had become bloated and outdated. Over time, it had been amended hundreds of times, growing into a document with more than 800 sections spread across 23 chapters. For taxpayers, professionals, and businesses, it was a confusing maze.
The Income Tax Act, 2025, is India’s attempt to start fresh:
- Simplification: Trimmed down to 536 sections.
- Digital-first features: Faceless assessments, online filing, and AI-driven scrutiny.
- Stability for individuals: The ₹12 lakh basic exemption limit remains intact, protecting the middle class.
- Adaptability: New rules to cover emerging industries like online gaming, fintech, and crypto assets.
Think of it as moving from an old flip phone to a modern smartphone. The basics are the same, but the new version is faster, smarter, and ready for the future.
Historical Evolution of India’s Tax Laws
This reform didn’t come out of nowhere. India’s tax laws have been evolving for decades.
- Pre-1961: India relied on colonial-era tax structures.
- 1961: The Income Tax Act consolidated tax rules into one comprehensive law.
- 1991: Economic liberalization introduced reforms to attract investment and simplify corporate taxes.
- 2016: The Goods and Services Tax (GST) restructured indirect taxes across the nation.
- 2025: The Income Tax Act, 2025 becomes the most sweeping reform in over six decades.
Other countries regularly overhaul their tax codes. For example, the U.S. passed the Tax Reform Act of 1986 and later the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. India, however, has historically been slower to modernize.
Other Bills Passed: Beyond Taxes
The tax reform took center stage, but it wasn’t the only change. Parliament approved 18 other significant bills:
- Indian Ports Bill – Modernizing port governance for global competitiveness.
- Merchant Shipping Bill – Updating maritime law for international standards.
- Sports Governance Bill – Overhauling administration of sports bodies, especially after controversies around transparency.
- Online Gaming Regulation Bill – Bringing legal clarity to a booming multi-billion-dollar industry.
Each of these bills could have sparked lively debate, but they slid through Parliament without much discussion.
Political Shock: Opposition Silence
Democracy thrives on debate. When bills pass without scrutiny, it raises eyebrows.
In the Lok Sabha, 12 bills passed without discussion. In the Rajya Sabha, 15 bills were approved amid noisy disruptions, but without structured debate. For the opposition, this silence may have been a strategy—or a sign of disarray.
Analysts point out that without debate, important questions go unanswered. For instance:
- How will digital-first tax assessments affect rural taxpayers with limited internet access?
- Will the new system truly reduce corruption, or just create new loopholes?
- Are businesses ready for compliance with emerging digital regulations?

Impact on Citizens and Businesses
Here’s how the new law could play out in real life:
Salaried Worker: Anita, an IT engineer in Bengaluru earning ₹15 lakh, now faces fewer forms and a simplified filing process. The ₹12 lakh exemption keeps her financial planning stable.
Small Business Owner: Ravi, who runs a café in Delhi, benefits from streamlined compliance. Instead of juggling multiple accountants, he can file digitally with less hassle.
Investor: Priya in Mumbai invests in stocks and crypto. The new act gives her clearer rules on taxation, reducing the fear of sudden penalties.
Economic and Professional Implications
- For Professionals: Accountants, tax consultants, and lawyers must quickly learn the new law. Training programs and certifications will become essential.
- For Businesses: Predictability and simplification make India a more attractive destination for investors.
- For Citizens: A clearer law reduces fear and confusion around taxes, potentially improving compliance.
Economists estimate that India could attract an additional $30 billion in foreign direct investment in 2026, thanks to the predictability of the new framework.
Expert Opinions
- Economists welcome simplification but caution that laws without debate often need amendments later.
- Policy experts warn that the silence of the opposition sets a dangerous precedent for democracy.
- Industry leaders are optimistic, saying a streamlined tax system is a “pro-business signal” to global markets.
According to a report in The Economic Times, tax consultants expect a “transition period of confusion” before the system stabilizes.
Global Comparison
When compared globally, India’s reforms stand out:
- USA: Tax reforms often take months of debate, with competing party priorities.
- UK: Parliament carefully debates each clause before passage.
- India 2025: Sweeping reforms passed in a matter of days, without substantial debate.
This speed is rare—and controversial.
What to Watch After April 2026?
The new law will be enforced starting April 1, 2026. Key things to watch:
- Implementation: Will the digital features work smoothly across India?
- Compliance: Will taxpayers adapt easily to faceless assessments?
- Amendments: Will loopholes appear that require future changes?
Practical Advice for Professionals
- Stay informed: Follow Income Tax India.
- Leverage digital tools: Invest in tax-filing software.
- Educate clients: Help small businesses and individuals adapt to the new rules.
- Anticipate changes: Expect clarifications and amendments after rollout.
Parliament Passes Two New Tax Bills — Here’s What That Means for Your Wallet
GST Fraud on the Rise: Towed Vehicles and Issued E-Way Bills—What the Authorities Are Hiding!








