Apollo Tyres Hit With ₹61.52 Lakh GST Demand: If you’ve been keeping an eye on Indian corporate tax news lately, you probably caught the headline: Apollo Tyres has been hit with a ₹61.52 lakh GST demand. We’re talking about one of India’s biggest tire manufacturers getting a notice from the Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes Department for allegedly claiming ineligible input tax credit (ITC). Now, if “input tax credit” sounds like confusing legal jargon, don’t worry — we’re going to break it down, explain why this matters, and share tips so that both everyday readers and tax professionals can understand the big picture.
Apollo Tyres Hit With ₹61.52 Lakh GST Demand
The ₹61.52 lakh GST demand against Apollo Tyres highlights an important truth: tax compliance is non-negotiable, and ITC rules leave little room for error. While this case is unlikely to affect Apollo’s bottom line, it’s a cautionary tale for businesses of all sizes to invest in compliance systems, vendor checks, and robust documentation. For Apollo, this is just another legal step in a long corporate journey. For the rest of us, it’s a reminder that the taxman is always watching — and that prevention is far cheaper than litigation.

| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Company | Apollo Tyres Limited |
| Authority Issuing Demand | Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes Department |
| Amount | ₹61.52 lakh (includes tax and penalty) |
| Reason | Alleged ineligible input tax credit |
| Date Issued | August 12, 2025 |
| Company Response | Plans to appeal before Appellate Authority |
| Impact on Business | Company says no material effect on operations |
| Official Website | https://corporate.apollotyres.com |
About Apollo Tyres
Founded in 1972 and headquartered in Gurugram, Apollo Tyres is a globally recognized tire brand, operating manufacturing plants in India, Hungary, and the Netherlands. The company supplies tires for passenger cars, trucks, buses, and agricultural vehicles. With a market capitalization in the billions, Apollo Tyres has a significant global presence, exporting to over 100 countries.
Its financial scale means even a ₹61.52 lakh tax dispute is relatively small in proportion to annual revenues — but these cases still attract attention because they can reveal patterns in compliance practices.
What Exactly Happened?
On August 12, 2025, the Deputy Commissioner of Commercial Taxes in Tamil Nadu issued a Goods and Services Tax (GST) demand order against Apollo Tyres. The allegation is that Apollo claimed input tax credits it wasn’t entitled to under GST law.
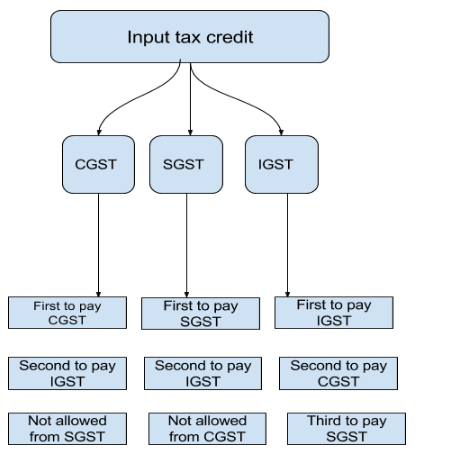
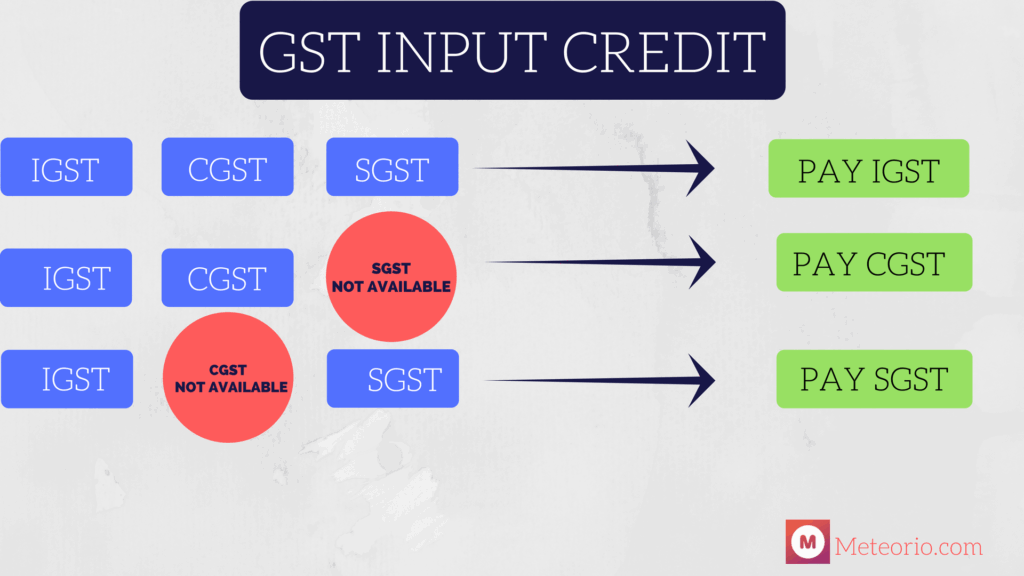
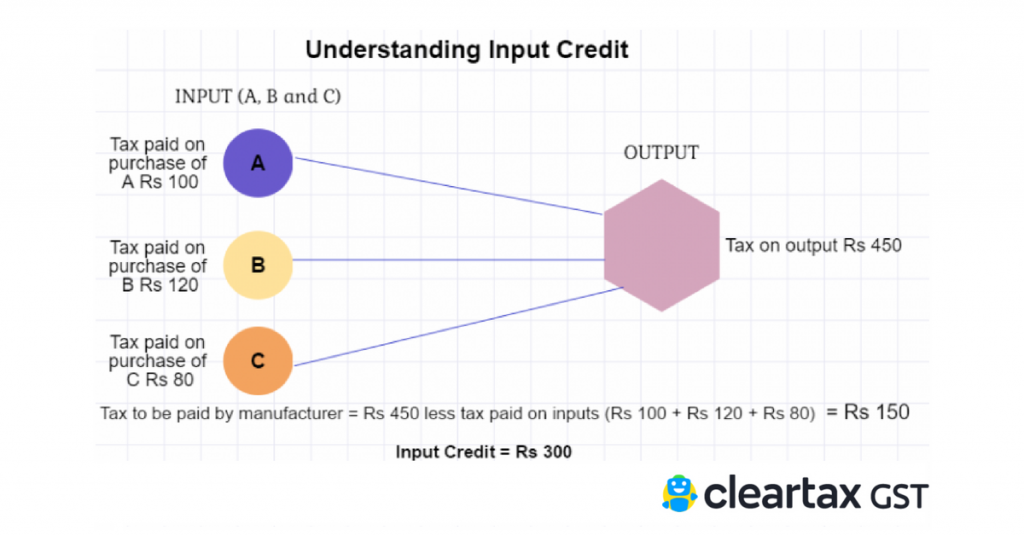
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a unified indirect tax on goods and services in India. Input Tax Credit (ITC) allows businesses to deduct the GST they paid on purchases from the GST they owe on sales.
Think of it as a store credit system: you get to subtract taxes you’ve already paid when buying inputs from the taxes you owe on selling finished goods. But if you try to claim credit for something ineligible — like a non-business purchase — the tax authorities can demand repayment, plus penalties.
Historical Context of GST Disputes
Since the rollout of GST in July 2017, ITC-related disputes have become one of the top enforcement areas for the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
According to CBIC’s 2024 annual report:
- Over ₹20,000 crore worth of disputes involved alleged wrongful ITC claims.
- Many cases stemmed from purchases from vendors who failed to remit GST.
- Automated invoice-matching (via GSTR-2B) has made detection faster.
One landmark case often cited is Kay Kay Industries vs. Commissioner of Central Excise (2013), where the Supreme Court of India ruled that businesses can’t claim tax credit if they fail to prove the tax was actually paid to the government.
Why Apollo Tyres Hit With ₹61.52 Lakh GST Demand? Understanding Ineligible ITC
“Ineligible ITC” refers to claiming credits that are not permitted under GST law. This can happen due to:
- Non-compliant vendors – Buying from suppliers who don’t file their GST returns.
- Non-business expenses – Claiming credits for items used for personal purposes.
- Documentation errors – Missing GSTIN, incorrect invoice details, or mismatched data.
- Expired timelines – Claiming ITC beyond the permissible time period (generally November 30 of the following year).
While Apollo Tyres has not disclosed the specific reason for this case, it falls into one of these common categories.
Past GST Disputes Faced by Apollo Tyres
This isn’t Apollo’s first time facing such a notice:
- April 2024 — ₹2.06 crore GST demand in Tamil Nadu over alleged ITC issues.
- November 2024 — ₹31.57 lakh GST demand in Rajasthan for disallowed ITC.
In both cases, Apollo appealed and stated the matters would not impact operations. The recurrence suggests the company’s vast scale and supplier network make it more prone to ITC disputes.
The Appeal Process in GST Disputes
Here’s how such disputes are handled in India:
- Notice Issued – Tax authorities issue a written demand detailing the alleged violation.
- Pre-deposit Requirement – To appeal, companies must deposit 10% of the disputed tax amount.
- Appeal to Appellate Authority – The first level of appeal under GST law.
- GSTAT and Courts – If not resolved, the matter can escalate to the Goods and Services Tax Appellate Tribunal, High Court, or Supreme Court.
These proceedings can take months to years, during which companies often continue business as usual.
Impact on Shareholders and Market Sentiment
From a shareholder perspective, the monetary amount here is negligible. However:
- Repeated disputes may cause analysts to question compliance frameworks.
- Investor sentiment can shift temporarily, even without material financial impact.
- Regulatory scrutiny can affect corporate image, especially for companies with global investors.
As of now, Apollo’s stock has not seen significant volatility following the announcement.
Industry Reaction and Expert Views
Tax experts say this case is a reminder that vendor compliance is just as important as internal compliance.
“Even if you follow the rules, if your supplier fails to pay GST or file returns, your ITC can be denied,” notes Ramesh Gupta, a GST consultant based in Chennai.
Industry groups like the Automotive Tyre Manufacturers’ Association (ATMA) have called for clearer rules and better technology integration between businesses and tax portals to reduce disputes.
Global Perspective: Similar Issues in the US
In the United States, a comparable situation would be claiming sales tax exemptions or federal tax credits without meeting eligibility criteria. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and state revenue departments regularly audit such claims.
Penalties in the US can include:
- Payment of back taxes.
- Interest on unpaid amounts.
- Civil or criminal penalties for fraud.
Like in India, the key defense is thorough documentation and proof of compliance.
Practical Compliance Strategies for Businesses
Whether you’re a multinational like Apollo Tyres or a small enterprise, these best practices can help avoid ITC disputes:
- Vendor Due Diligence
- Verify GST registration and filing status regularly via the GST portal.
- Include GST compliance clauses in vendor contracts.
- Invoice Matching
- Use software to match purchase invoices with GSTR-2B monthly.
- Address mismatches before filing returns.
- Documentation Discipline
- Keep physical and digital copies of all invoices, contracts, and payment proofs.
- Maintain a centralized compliance record.
- Timely Claims
- Track ITC deadlines to avoid losing eligibility.
- Employee Training
- Train finance and procurement teams on GST compliance basics.
Common Mistakes That Trigger GST Audits
- Claiming ITC for blocked credits (like motor vehicles for personal use).
- Not reversing ITC when goods are returned or scrapped.
- Mismatched GSTINs between invoices and returns.
- Delayed filing of GST returns.
Vodafone Idea Faces ₹21.39 Crore GST Penalty for Alleged Short Payment Under RCM!
GST Council Considers Amnesty That Could Save Small Businesses Lakhs in Penalties










