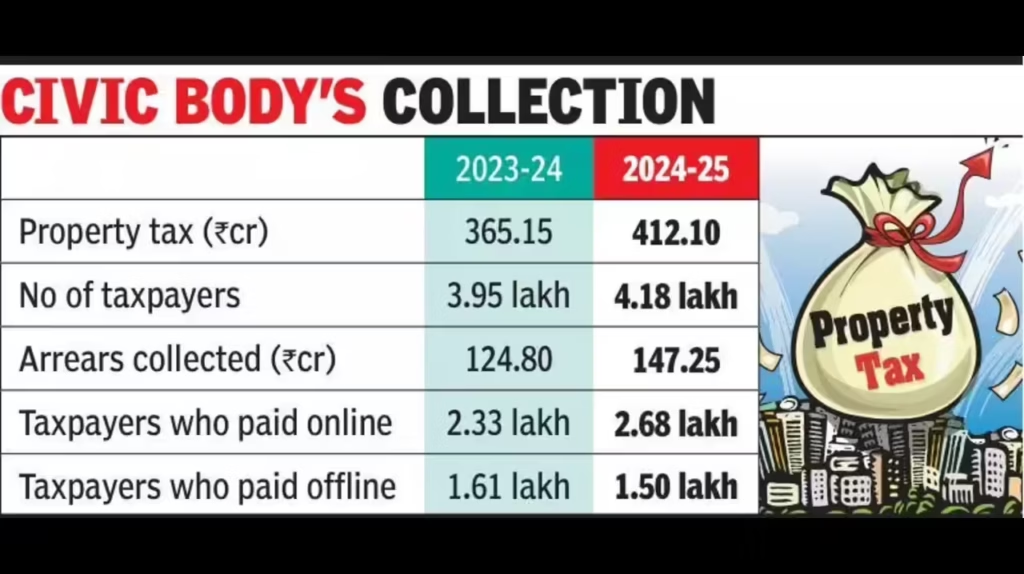
Government Institutions Named Among Top Tax Defaulters: In Rajkot, Gujarat, government institutions have emerged as some of the top property tax defaulters, creating ripples across civic circles. The Rajkot Municipal Corporation (RMC) relies heavily on property tax collection to fund essential services like road maintenance, sanitation, and local infrastructure. However, with some government bodies failing to pay their dues, the municipality faces serious financial strain. This situation has prompted debates about accountability, governance, and strategies to improve tax compliance, not just in Rajkot but across India.
Property tax, often considered a routine obligation for citizens, becomes a significant revenue source for local authorities. When large institutions—especially government offices—default on their taxes, it highlights gaps in administrative oversight and the need for stricter enforcement. The RMC has responded by issuing notices, sealing properties, and considering legal actions to recover dues. In this article, we’ll break down the issue, provide practical advice for citizens, and explore strategies to improve municipal revenue collection.
Government Institutions Named Among Top Tax Defaulters
The identification of government institutions among the top property tax defaulters in Rajkot underscores a broader challenge in municipal governance. While the RMC has taken steps to enforce compliance, the solution requires sustained efforts, transparency, and active citizen participation. Ensuring timely payment of property taxes will help improve civic services, accelerate infrastructure development, and maintain trust between government authorities and the public. Addressing government defaults not only stabilizes municipal finances but also sets an example for other institutions. By combining enforcement, public awareness, and efficient payment systems, Rajkot can strengthen its fiscal health while fostering accountability in governance.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Defaulters Identified | Government institutions such as the Office of the DSP, Gymkhana Club, Shakti Bhavan, Shalimar Mall, and Police Community Club. |
| Outstanding Dues | Exact figures are not publicly disclosed, but unpaid dues are substantial enough to affect RMC’s finances. |
| RMC’s Response | Issued notices, sealed properties, and is considering legal proceedings including auctions to recover dues. |
| Impact on Civic Services | Reduced revenue may delay infrastructure projects, sanitation services, and other public amenities. |
| Public Reaction | Citizens have expressed frustration over lack of accountability and inconsistent enforcement of tax rules. |
Understanding Property Tax in India and Rajkot
Property tax is a mandatory levy imposed by municipal authorities on property owners. The tax amount is generally based on factors like property size, location, usage (residential or commercial), and government-assessed property value. In cities like Rajkot, property tax forms a significant portion of municipal revenue. This income is crucial for funding public infrastructure such as roads, street lighting, parks, hospitals, and schools.
In Rajkot, the RMC is responsible for collecting property tax from residential, commercial, and institutional properties. The process involves:
- Property Assessment: The RMC evaluates the property based on its area, type, location, and occupancy.
- Tax Computation: Using the assessment, the tax department calculates the annual tax due.
- Notice and Payment: Property owners receive a notice detailing the tax amount, due dates, and any discounts for early payment.
- Enforcement Measures: For non-payment, the RMC can impose penalties, interest, and initiate legal action including property sealing or auctions.
Failure to collect taxes from large institutions, especially government offices, can create a significant revenue shortfall, affecting public services for citizens.
Why Government Institutions Named Among Top Tax Defaulters?
The non-payment of property taxes by government institutions in Rajkot can be attributed to multiple factors:
- Budget Constraints: Certain government offices may face limited budget allocations, causing delays in fulfilling obligations like property tax.
- Administrative Oversight: Bureaucratic inefficiencies and communication gaps can result in lapses in paying taxes on time.
- Historical Practices: Some institutions have historically believed they are exempt or entitled to leniency.
- Lack of Accountability: Weak enforcement mechanisms often reduce the urgency to pay dues promptly.
Similar trends have been observed in other Indian cities. For example, in Ranchi, government institutions like the Heavy Engineering Corporation owed significant dues, highlighting a systemic problem across municipal bodies.
Consequences of Non-Payment
Non-payment of property tax by major institutions affects multiple stakeholders:
- Financial Strain on RMC: Reduced revenue directly impacts the municipality’s ability to fund essential services.
- Delayed Infrastructure Projects: Planned roads, parks, and sanitation projects may face delays, affecting citizens’ quality of life.
- Public Discontent: Citizens may feel the government is not enforcing rules fairly, eroding trust in local authorities.
- Negative Economic Impact: Lower revenue can limit investment in urban development, reducing overall economic growth in Rajkot.
RMC’s Measures to Address the Issue
The Rajkot Municipal Corporation has implemented several measures to tackle tax defaulters:
- Issuance of Notices: The RMC sends official reminders demanding payment of overdue property taxes.
- Sealing of Properties: Properties with long-standing dues may be sealed until taxes are cleared.
- Legal Actions: The municipality is considering auctions of properties belonging to defaulters to recover dues.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: The RMC is encouraging transparency by publishing lists of defaulters to increase social accountability.
These actions aim to balance enforcement with fairness, ensuring that institutions pay dues while giving them reasonable opportunity to comply.
Case Studies: Government Defaulters in Rajkot
- Office of the DSP: The office reportedly delayed payments for multiple fiscal years.
- Gymkhana Club: Recognized for its recreational facilities, this institution has accumulated unpaid taxes over several years.
- Shakti Bhavan: A government office that faced enforcement notices for its dues.
- Shalimar Mall: A commercial property managed by a government agency that also appeared on the defaulters’ list.
- Police Community Club: Dues from this facility illustrate that even essential service organizations are not immune from lapses.
These examples show that non-payment spans residential, commercial, and institutional sectors, emphasizing the need for strict enforcement policies.
Practical Advice for Citizens
Citizens can play a proactive role in improving property tax compliance and municipal revenue collection:
- Check Your Property Tax Status: Visit the RMC official portal to verify your payment status and clear dues promptly.
- Set Up Online Payments: Automating payments reduces the risk of missing deadlines and ensures continuous service.
- Participate in Awareness Campaigns: Educating neighbors and communities about the importance of property tax can improve collective compliance.
- Engage with Authorities: Attend local municipal meetings or submit feedback to advocate for stricter enforcement on defaulters.
- Report Defaults: Citizens can confidentially report institutions that are not paying taxes, ensuring accountability.
Comparisons with Other Cities
Comparing Rajkot with other Indian cities highlights key lessons:
- Chandigarh: Panjab University owes over ₹68 crore in property taxes. The municipal corporation issued legal notices and applied penalties, showing that transparency and enforcement work hand-in-hand.
- Ranchi: The Ranchi Municipal Corporation identified government offices with dues totaling over ₹60 crore. Legal action was considered to recover the funds.
- Ahmedabad: The municipal corporation initiated property auctions for persistent defaulters, improving collection rates significantly.
These examples suggest that publicizing defaulters and combining legal enforcement with citizen engagement are effective strategies.
Property Tax Shock? Madurai Corporation Submits Action Plan to High Court
Deadline Extended: Property Tax Defaulters Get Time Till August 31 to Settle Dues
How the Mughals Collected Taxes — From Crops to Roads, Here’s What You Paid Back Then










