Income Tax Guide: When tax season rolls around, there’s often one thing that causes a lot of headaches for taxpayers—foreign assets. Whether it’s a savings account across the border, an investment in a foreign stock, or property owned in another country, reporting foreign assets on your Income Tax Return (ITR) for Assessment Year (AY) 2025-26 is crucial for compliance. If you fail to report these assets properly, you risk facing heavy penalties, interest, or even jail time. But don’t worry! This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, in simple, easy-to-understand steps. Foreign assets are a reality for many people today. With global investments and international banking becoming more common, understanding how to report these foreign assets can seem overwhelming. The good news is, it doesn’t have to be that way. We’ll break everything down—step by step—so that you can handle your tax filing like a pro, stay on the right side of the law, and avoid unwanted surprises.
Income Tax Guide
Reporting foreign assets in your ITR for AY 2025-26 doesn’t have to be a nightmare. By following the step-by-step process outlined above, you can ensure you’re on the right side of the law and avoid penalties. Remember to keep accurate records, use official exchange rates, and disclose all your foreign holdings, no matter how small. The key takeaway here is to be thorough and transparent when it comes to foreign assets. The government is strict about non-disclosure, but with a little attention to detail, you can easily navigate this part of your tax filing and keep your finances in order.

| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Relevant Tax Form | ITR-2 for individuals with foreign assets |
| Mandatory Disclosure | Schedule FA |
| Foreign Asset Categories | Bank Accounts, Property, Shares, Trusts, Foreign Insurance Contracts, and more |
| Currency Conversion | Report in INR, using the official exchange rates (SBI TTBR) at the time of transaction or balance peak |
| Penalties for Non-Compliance | Penalty up to ₹10 lakh per undisclosed asset, and up to 7 years of imprisonment for willful evasion |
| Filing Deadline | September 15, 2025 (Revised Return until December 31, 2025) |
| Official Resources | Income Tax Portal |
Why Is Reporting Foreign Assets Important?
Many individuals, especially those who have international ties, may own assets in foreign countries. Whether you have a foreign bank account, stock holdings, or property abroad, it’s essential to report these assets in your Income Tax Return (ITR). This is required by the Income Tax Department of India to ensure transparency, track income, and prevent tax evasion.
For Indian taxpayers who are Resident and Ordinarily Resident (ROR), disclosing foreign assets is a legal requirement. Under the Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015, non-disclosure can lead to severe penalties, including fines, interest, or even imprisonment. The government has been cracking down on those who fail to disclose their foreign assets, with an emphasis on tracking hidden income stashed overseas.
So, let’s dive deeper into the specifics of how to report these assets correctly in your tax filing for AY 2025-26.
Step-by-Step Income Tax Guide on How to Report Foreign Assets in ITR AY 2025-26
Step 1: Know Which Form to Use (ITR-2)
The first step in reporting foreign assets is knowing which tax form to use. If you’re an individual who holds foreign assets, you’ll need to file ITR-2. This form is specifically designed for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) who do not have income from business or profession but may have income from salary, capital gains, or foreign assets.
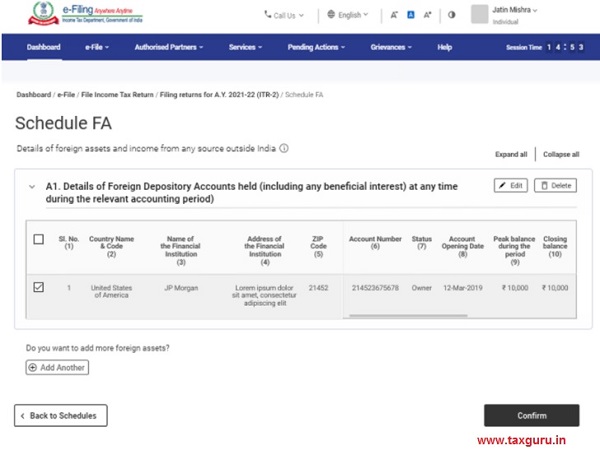
Step 2: Locate and Complete Schedule FA
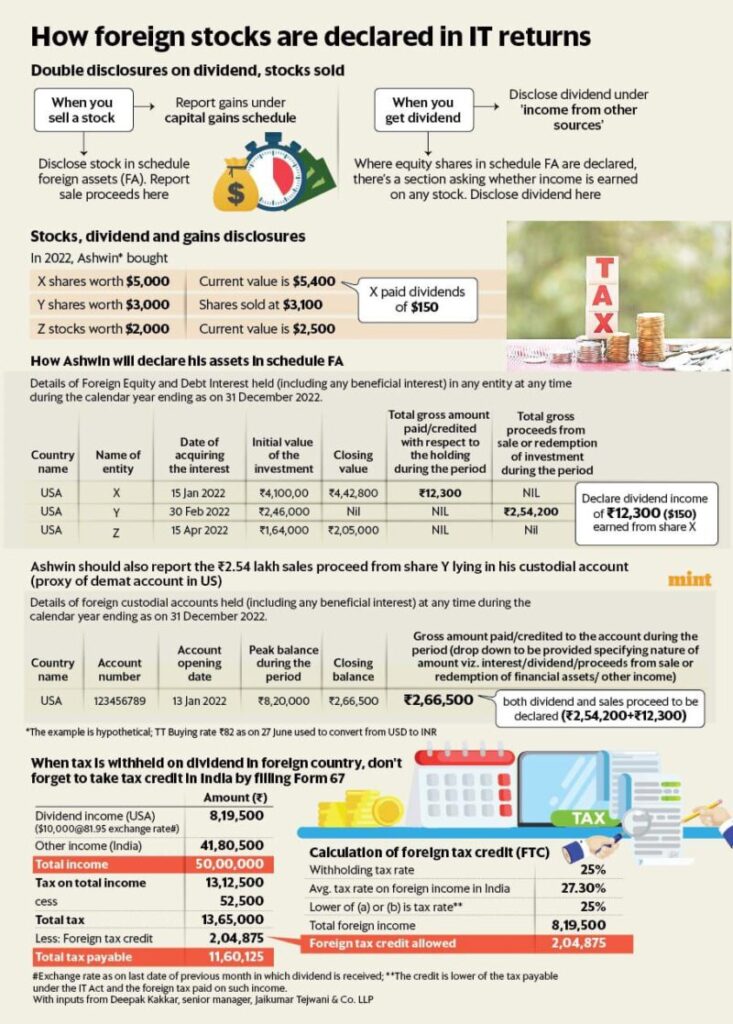
Once you’ve selected the appropriate form, the next task is to fill out Schedule FA. This section of the ITR form is where you’ll provide details about your foreign assets. It includes the following categories:
- Foreign Depository Accounts (e.g., savings or checking accounts in foreign banks)
- Foreign Custodial Accounts (e.g., investment accounts)
- Foreign Equity and Debt Instruments (e.g., foreign stocks or bonds)
- Foreign Life Insurance Contracts (if applicable)
- Immovable Property Outside India (e.g., real estate)
- Other Capital Assets (e.g., vehicles or jewelry)
- Financial Interest in Foreign Entities (if you own a part of a foreign company or trust)
You must report the value of these assets as of December 31, 2024 (the last day of the calendar year), converting everything into Indian Rupees (INR) using the Telegraphic Transfer Buying Rate (TTBR) from the State Bank of India.
Step 3: Convert Foreign Assets to INR
All your foreign assets, whether it’s a bank balance or a piece of property, need to be reported in Indian Rupees. To do this, you’ll need to use the official exchange rate provided by the State Bank of India (SBI). This could be the exchange rate at the time of transaction, the peak balance date, or December 31, 2024 if you held the asset throughout the year.
For example, if you held a foreign bank account with a peak balance of $10,000 in 2024, you’d need to look up the SBI TTBR on December 31, 2024, and use that rate to convert the dollar amount into INR.
Step 4: Declare Income from Foreign Assets
In addition to reporting the assets themselves, you also need to declare any income generated from them. This could include:
- Interest earned from foreign bank accounts
- Dividends from foreign stocks
- Rental income from foreign property
This income must also be reported in Schedule FSI of the ITR, and again, it needs to be converted into INR using the appropriate exchange rates.
Step 5: Submit Your Tax Return
Once you’ve filled out the ITR-2 form, including Schedule FA and FSI, double-check your details. After that, it’s time to submit your return electronically through the Income Tax Portal.
Government Notifies Income Tax Act 2025 Effective April 1
Income Tax Rules Revised — Salaried Employees to Get Higher Perquisite Limits
Online Gaming Income FY25 – Tax Rate, TDS Rules And ITR Reporting Explained
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Reporting Foreign Assets
While the process is straightforward, there are several common mistakes that taxpayers make when reporting foreign assets:
- Not Reporting All Assets: It’s easy to forget about dormant foreign accounts or assets held jointly with others. All assets, regardless of activity, need to be disclosed.
- Incorrect Currency Conversion: Using unofficial or outdated exchange rates can cause discrepancies. Stick to the official rates to avoid issues.
- Missed Income: Don’t forget to report income from foreign assets, whether it’s interest, dividends, or rent. Missing this can trigger penalties.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you’ll ensure a smoother filing process and stay compliant.










