India Fires Back at Trump’s 50% Tariffs With GST Cuts and Bold Reforms: When the headlines screamed that India fires back at Trump’s 50% tariffs with GST cuts and bold reforms, it wasn’t just noise. This is a turning point in U.S.–India trade relations and potentially a reshaping of the global economy. Washington came in swinging with a massive tariff hike, and New Delhi responded not by retreating, but by rolling out reforms that could strengthen its domestic economy in the long run. This isn’t your everyday trade tiff. We’re talking about one of the world’s largest democracies facing off with another, each with billions of dollars at stake. Whether you’re a professional analyzing markets, a small-business owner shipping products, or just a curious reader, the impact of this move is far-reaching. Let’s break it down in plain English—with facts, stats, and some straight talk.
India Fires Back at Trump’s 50% Tariffs With GST Cuts and Bold Reforms
India’s answer to Trump’s 50% tariffs is not just defensive—it’s transformative. By slashing GST, cutting red tape, and boosting domestic consumption, New Delhi is signaling that it won’t be cornered. Instead, it’s using this challenge as a chance to reform and future-proof its economy. For the U.S., tariffs may protect some jobs but will likely raise prices for consumers. For India, the strategy is clear: build resilience, reduce dependence, and keep growing. The big takeaway? In global trade, you can’t stop storms from coming, but you can decide whether you sink—or learn how to surf the waves.

| Point | Details |
|---|---|
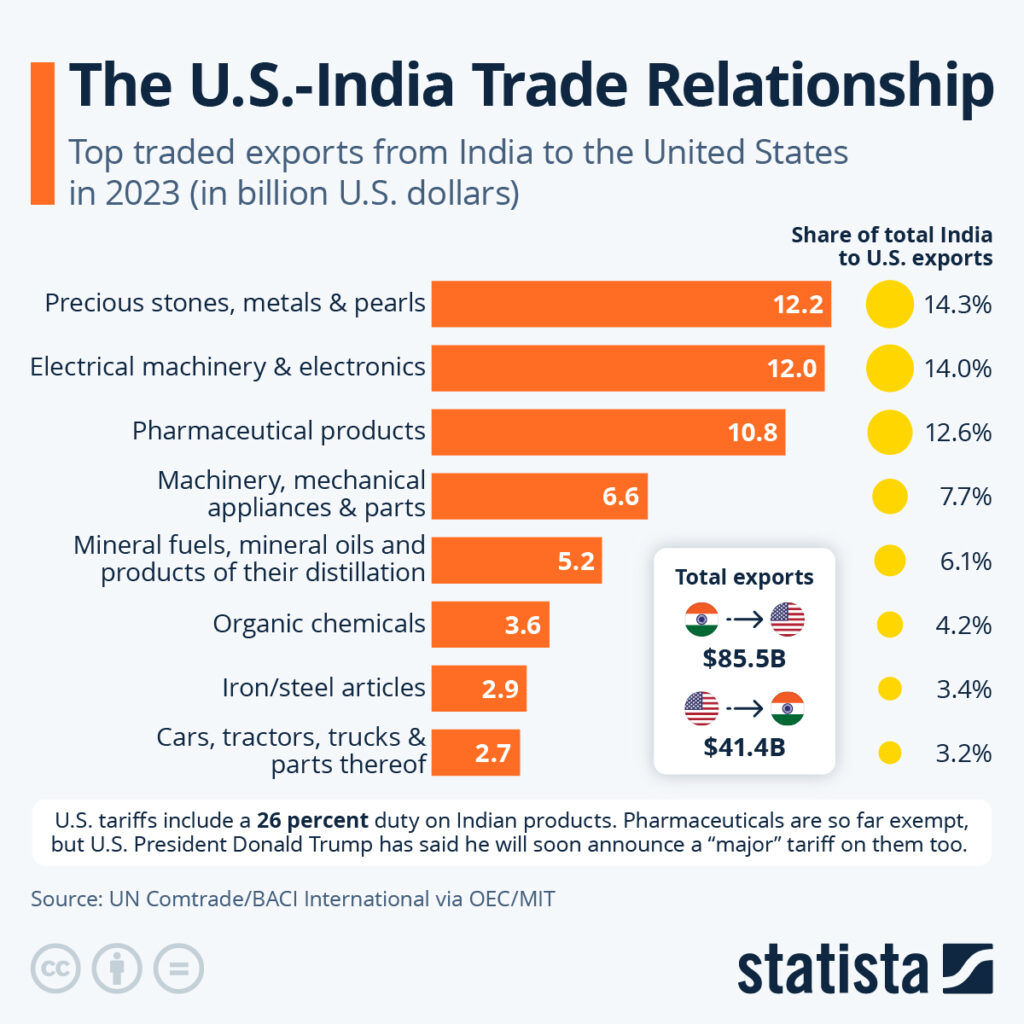
| U.S. Tariffs | Trump imposed a 50% tariff on Indian exports such as textiles, gems, seafood, and leather. Pharma and electronics were exempt. |
| Effective Rate | Economists say the true impact is 33.6% since not all exports are affected equally. |
| GDP Drag | Tariffs could reduce India’s GDP growth by 0.7% in one year if sustained. |
| GST Overhaul | India cut GST to just two slabs (5% and 18%), expected to boost demand by ₹5.31 lakh crore ($64B). |
| Reform Drive | Includes income tax cuts, deregulation, and export promotion measures worth ₹25,000 crore. |
| Growth Outlook | Despite tariffs, India is still forecast to grow 5.8% in FY2025/26 and 5.4% in FY2026/27. |
| Official Resource | Ministry of Finance, Govt. of India |
The Tariff Shock: What Happened
On August 27, 2025, the U.S. government hit Indian exports with a 50% tariff. The reason? Washington cited India’s continued import of Russian crude oil and the need to address America’s growing trade deficit.
The sectors most affected are labor-intensive industries:
- Textiles and garments
- Gems and jewelry
- Leather goods
- Seafood exports
Together, these industries employ millions of workers, many in small and medium enterprises. The tariff was designed to put pressure directly on these job-heavy sectors.
But not everything was targeted. Pharma, electronics, and petroleum products—three of India’s top export earners—were exempt. That spared India from a total collapse in trade revenues.
Why It Matters: Economic Ripples
Economists estimate that the effective tariff impact is 33.6%, not the full 50%, because exemptions soften the blow. Still, that’s enough to reduce India’s GDP growth by 0.7 percentage points if the tariffs stay for a year.
For India, that’s like slowing a race car down on a straight track. Growth was expected to stay above 6%, but now forecasts are revised closer to 5.8% in FY2025/26. Even with that slowdown, India remains one of the fastest-growing major economies in Asia.
For the U.S., the tariffs mean some products—like Indian clothes at Walmart or shrimp at Costco—are going to cost more. Tariffs usually translate to higher prices for American consumers, even if politicians pitch them as protecting local jobs.
India’s Counter-Move: GST Cuts and Reforms
Rather than retaliate with its own tariffs, India went inward—choosing reforms over reaction. This is where things get interesting.
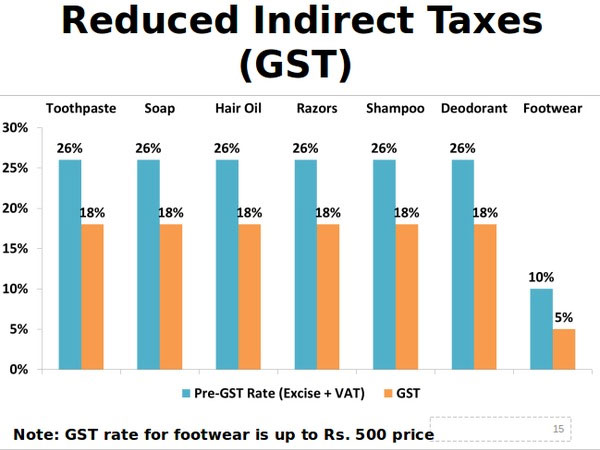
GST Overhaul
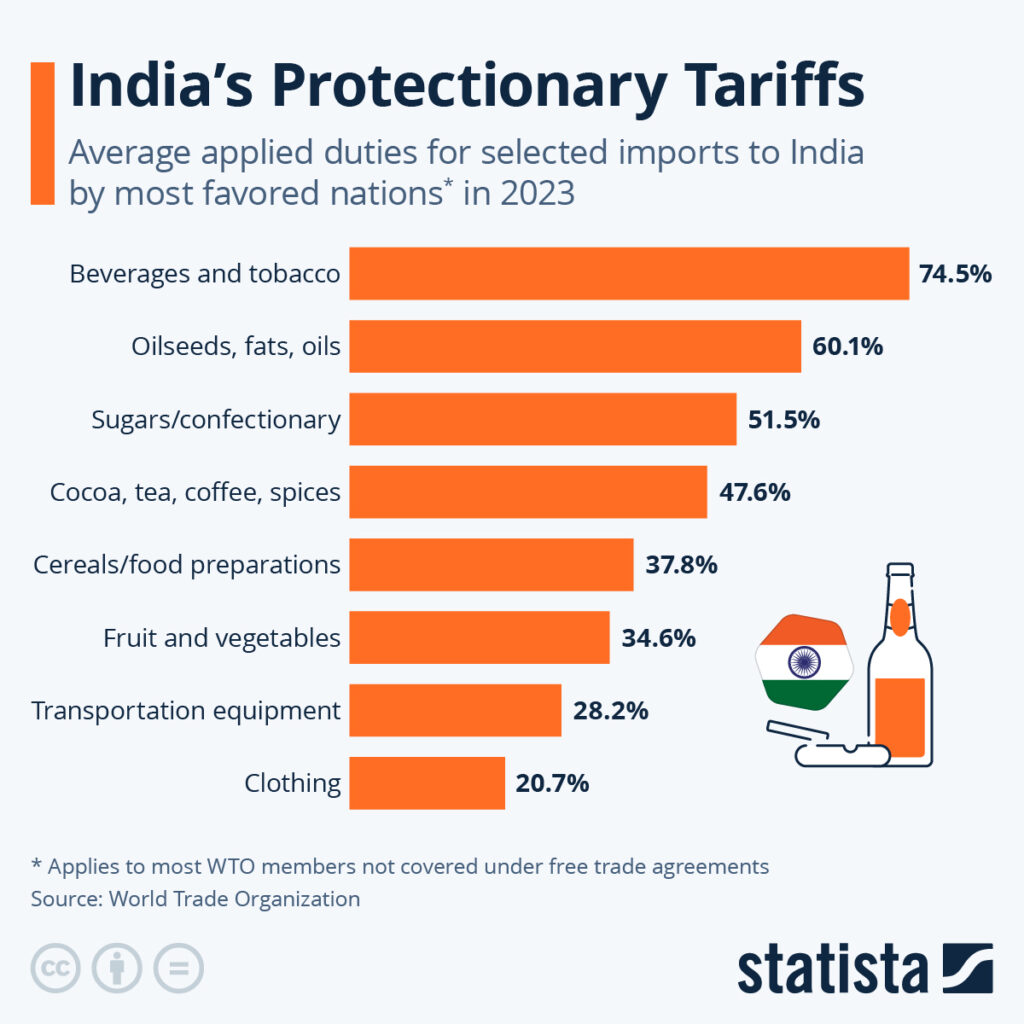
India simplified its Goods and Services Tax (GST) system from four tax brackets to just two: 5% and 18%.
That means:
- Consumer goods like appliances and durables now face lower taxes.
- Small businesses deal with less paperwork.
- Demand gets a boost as products become cheaper.
According to SBI Research, these reforms, combined with income tax cuts, could generate ₹5.31 lakh crore ($64B) in additional spending power—roughly 1.6% of GDP.
Cutting Red Tape
Committees led by senior policymakers are eliminating outdated regulations and laws. By reducing bureaucracy, India hopes to make it easier for businesses to invest and expand. This reform push includes:
- Scrapping colonial-era business laws.
- Faster approvals for startups and investors.
- A ₹25,000 crore export promotion fund to help small firms survive the tariff storm.
Export Diversification
India is now actively seeking new markets outside the U.S. Europe, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America are in focus.
For example:
- Surat’s diamond industry is redirecting exports toward Dubai and Hong Kong.
- Kerala’s seafood industry is ramping up exports to Japan and South Korea.
- Textile hubs in Tamil Nadu are exploring online sales through global e-commerce platforms.
RBI’s Safety Net
The Reserve Bank of India has pledged to keep liquidity flowing in case businesses run into trouble. Extra cash and credit support will ensure that exporters don’t collapse under tariff pressures.
Political Messaging
Prime Minister Modi used his Independence Day speech to reinforce the idea of Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India). The message: tariffs may hurt, but India will protect farmers, local industries, and small businesses while strengthening domestic production.
Real-World Impact of India Fires Back at Trump’s 50% Tariffs With GST Cuts and Bold Reforms
To understand how this plays out, let’s look at everyday examples:
- A leather goods exporter in Kanpur might shift sales from the U.S. to Africa, while applying for subsidies to cushion losses.
- A shrimp farmer in Kerala may now find new buyers in Japan, but at the cost of higher shipping expenses.
- A textile mill in Tirupur could pivot to e-commerce platforms like Amazon Global, reducing reliance on bulk U.S. orders.
For millions of workers in these sectors, the reforms and support measures could be the difference between keeping a job or facing layoffs.
Lessons From History
This isn’t the first time U.S.–India trade has faced turbulence. Back in 2018, Trump’s steel and aluminum tariffs hit India. In 2019, the U.S. removed India from the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP), eliminating duty-free access for $5.7B worth of exports.
Each time, India found ways to adapt. The difference now is that the tariffs are sharper, and the reforms in response are broader. Instead of patchwork fixes, India is using this crisis to overhaul its tax system, clean up regulations, and push for self-reliance.
The Geopolitical Angle
This tariff clash is also about geopolitics. The U.S. wants India to align more closely with its policies on Russia. At the same time, India sees this as an opportunity to deepen ties with Europe, Africa, and Asia.
By diversifying export markets, India reduces its dependence on both the U.S. and China. That’s a strategic move in a world where trade often doubles as political leverage.
Practical Guide: What Businesses Should Do
For Indian Exporters
- Diversify buyers—look beyond the U.S.
- Apply for government support through export promotion schemes.
- Embrace digital platforms for global sales.
For U.S. Importers and Retailers
- Prepare for higher costs in goods like apparel and seafood.
- Seek alternative sourcing from countries like Vietnam and Bangladesh.
- Work closely with Indian suppliers to share tariff burdens.
For Investors
- Focus on sectors like banking, consumer goods, and FMCG in India.
- Watch currency trends—the rupee could fluctuate under tariff stress.
- Look at long-term reforms as opportunities, not short-term shocks.
Expert Opinions
- Nomura Research: “The effective tariff is 33.6%, not 50%, but it still carries a significant economic cost.”
- Fitch Ratings: “Despite the tariffs, India remains resilient, with GDP growth expected above 5%.”
- Local Analysts: “GST cuts will cushion the impact by boosting household consumption, especially in urban markets.”
Why 15,200 Hospitals Stopped Cashless Treatment For Bajaj Allianz Policyholders
Europe Blocks U.S.-Bound Parcels – Tax Rule Change Behind The Move










