India On the Edge of Crypto Tax Reform: When it comes to crypto tax reform, India is making big moves that could change the way millions of investors, traders, and businesses interact with digital assets. If you’re holding Bitcoin, Ethereum, or even Dogecoin, the decisions coming out of New Delhi may hit your digital wallet sooner than you think. Right now, India is walking a fine line—encouraging innovation while trying to keep tax revenues flowing. With over 1.4 billion people, a booming startup scene, and one of the world’s largest crypto communities, the stakes couldn’t be higher.
India On the Edge of Crypto Tax Reform
India’s crypto tax regime is among the toughest in the world, but reform is on the horizon. The government is finally listening to industry voices, and changes like lower TDS, loss offsetting, and fairer rates could soon arrive. For now, compliance is key. Keep records, file taxes correctly, and plan ahead. Whether you’re a beginner stacking sats or a professional investor, the coming reforms could redefine how you manage your digital wallet in India.

| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Flat Tax Rate | 30% on crypto gains + 4% cess, no distinction between short/long term (CBDT official site) |
| 1% TDS Rule | Every transaction taxed, even if no profit; seen as major liquidity killer |
| Loss Offsetting | Not allowed—losses on one coin can’t reduce taxes on gains from another |
| Compliance Tools | AI, blockchain forensics, and wallet audits now part of enforcement |
| Global Standard | India moving toward OECD’s Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) |
| Proposed Reforms | Possible reduction of TDS to 0.1% and reconsideration of flat 30% tax |
A Quick Look Back: India’s Crypto Journey
India’s relationship with crypto has been a roller coaster:
- 2013 – The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues its first warning about Bitcoin.
- 2018 – RBI bans banks from dealing with crypto exchanges, effectively choking the industry.
- 2020 – Supreme Court lifts the ban, sparking a new boom in crypto adoption.
- 2022 – Government introduces 30% tax on gains and 1% TDS, shocking investors.
- 2025 – Talks of crypto tax reform begin, as industry pushback and global competition mount.
This history explains why today’s debate is so important. India has swung from banning crypto to taxing it heavily, and now possibly softening its stance.
Breaking Down India On the Edge of Crypto Tax Reform
For folks new to this, here’s a simple, no-jargon breakdown:
1. Flat 30% Tax on Gains
- No difference between short-term or long-term.
- Example: Buy ETH at $1,000, sell at $1,500 → Gain $500. Tax = $150 + cess.
2. 1% TDS on Every Trade
- Applies whether you profit or not.
- Example: Trade $10,000 across multiple coins in a month → $100 lost to TDS.
3. No Offsetting Losses
- If you lose $200 on Solana but gain $500 on Bitcoin, you still pay tax on the full $500.
4. GST on Services
- Since July 2025, 18% GST on exchange fees is in play.
How India Compares Globally?
To put things in perspective:
- United States – Crypto treated as property. Capital gains tax ranges 10–37%, but loss harvesting allowed.
- United Kingdom – Gains taxed at 10% or 20%, depending on income. Allowances for small gains.
- Singapore – No capital gains tax, making it a crypto hub.
- Japan – Crypto profits taxed as miscellaneous income at rates up to 55%, but losses can offset gains.
- India – Harshest setup: flat 30% tax, no loss offsetting, plus 1% TDS.
That’s why traders are jumping ship to Dubai or Singapore, where tax regimes are friendlier.
The Push for Change
Crypto exchanges like CoinSwitch and WazirX, along with global players like Binance, are lobbying the government. Their demands include:
- Cutting TDS from 1% → 0.1% to boost liquidity.
- Allowing loss offsets like in traditional stock trading.
- Reviewing the flat 30% rule, which is harsher than gambling taxes.
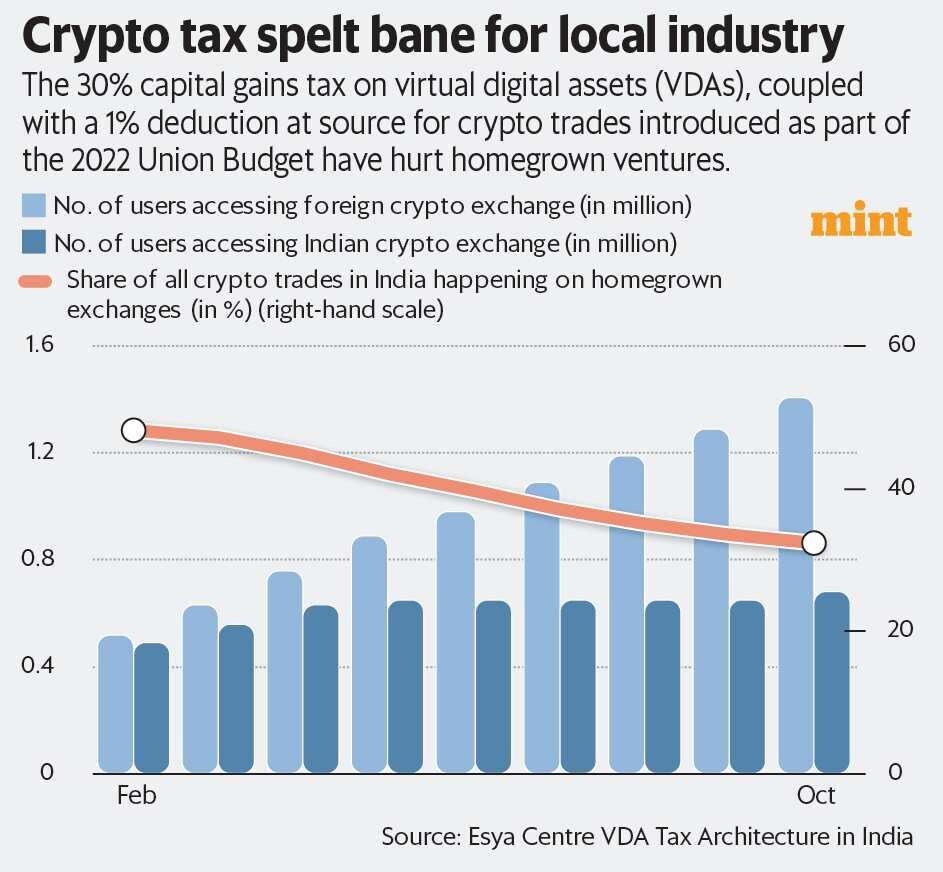
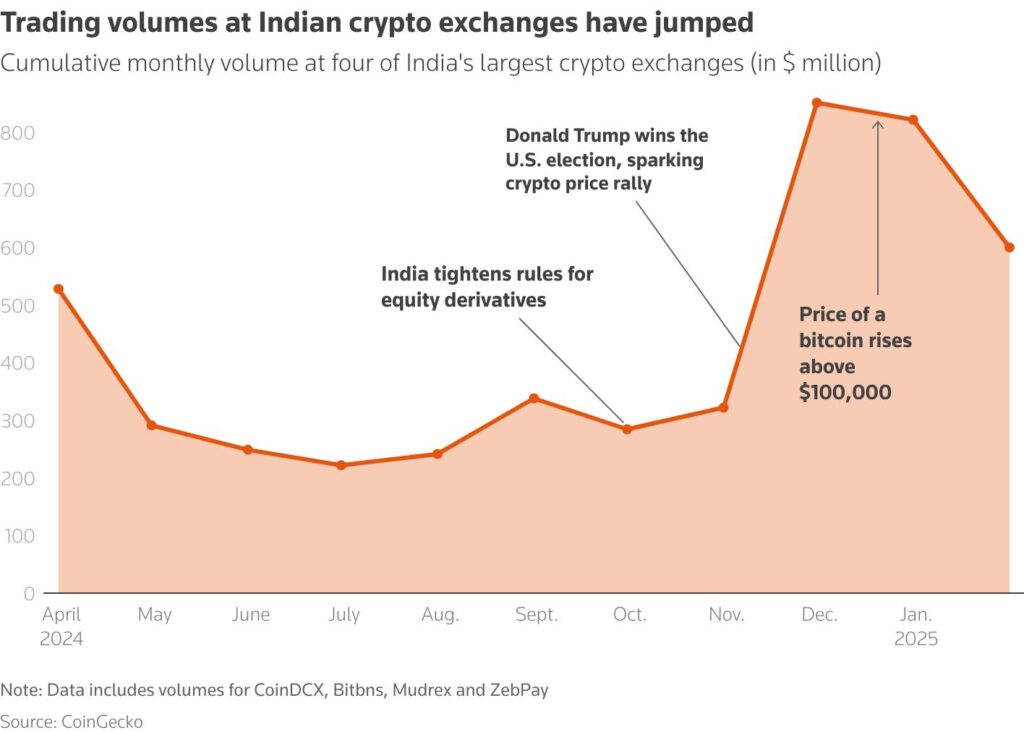
Since 2022, when the rules came in, trading volumes dropped more than 70% on Indian exchanges. The number of active traders fell from about 10 million to less than 3 million by late 2024. That’s bad for business, bad for innovation, and ironically, bad for tax collection.
What It Means for Your Digital Wallet?
Here’s where things get personal:
- Lower Transaction Costs – A TDS cut means you keep more money in your wallet.
- Better Planning – Loss offsetting could allow smart tax strategies.
- More Scrutiny – With AI and blockchain forensics, expect zero room for “under the table” trading.
- Global Data Sharing – Under CARF, even offshore wallets may no longer stay hidden.
Real-Life Scenarios
Case 1: The Small Trader
Ravi buys Bitcoin worth $1,000. He sells it at $1,200. Profit = $200.
- Current tax: 30% = $60 + cess, plus 1% TDS already deducted.
- If reforms allow loss offsetting, Ravi could reduce future gains with losses.
Case 2: The Whale
Anita trades $1 million worth of crypto monthly. Even at 0% profit, she loses $10,000 monthly to TDS. If cut to 0.1%, losses drop to just $1,000—a game-changer.
Impact on Startups and Businesses
The Indian Web3 ecosystem is massive—over 450+ startups operate in blockchain, NFTs, and DeFi. But high taxes are pushing:
- Talent overseas → Developers moving to Singapore, Dubai.
- Exchanges offshore → Many shifting headquarters abroad.
- Investors wary → Venture capitalists cautious about India’s hostile tax regime.
A 2024 survey by LocalCircles found that 76% of Indian crypto users reduced trading after the tax rules, and 41% shifted to overseas exchanges. Reforms could reverse this capital flight and bring billions back into India’s ecosystem.
Step-by-Step Guide: Handling Crypto Taxes in India
Step 1: Keep Records
Track all trades using apps like CoinTracker or Koinly.
Step 2: Calculate Gains
Formula = Sale Price – Buy Price. Apply 30% + cess, minus TDS paid.
Step 3: File With Schedule VDA
New section in ITR (from FY 2025-26) requires detailed crypto reporting.
Step 4: Stay Updated
Follow CBDT updates and trusted media like Economic Times or CoinDesk.
Step 5: Plan Smart
Consider long-term holding, staking, or portfolio diversification.
Future Outlook: What Experts Predict
- Short-Term: TDS likely cut to 0.1% to improve liquidity.
- Medium-Term: Possible allowance for loss offsets, making crypto similar to stocks.
- Long-Term: India may move toward a balanced tax regime aligned with OECD standards.
Analysts also predict that India could adopt a progressive tax model like the U.S., where tax rates depend on income brackets. If implemented, small traders would pay less while whales still contribute a fair share.
Investor Tips & Warnings
Do keep trade logs and use trusted exchanges.
Do pay attention to CBDT circulars and ITR deadlines.
Do consider professional tax advisors if you trade heavily.
Don’t rely on offshore wallets to stay hidden—CARF is closing that gap.
Don’t assume crypto taxes = stock taxes—they’re treated differently.
Don’t wait until tax season—plan throughout the year.
India@100: Why Experts Say Fixing GST Could Unlock a Health Insurance Boom
2025 Tax Slabs Revealed: Find Out How Much You’ll Really Pay










