India’s Manufacturing Boom Pushes July GST Inflows: India’s manufacturing boom pushes July GST inflows up by 7.5 percent, signaling not only a healthy tax collection cycle but also a strong pulse in the country’s industrial growth. In July 2025, Goods and Services Tax (GST) collections hit ₹1.96 lakh crore (~$23.5 billion USD), marking a notable rise from the same time last year. While GST is often viewed as a technical metric, it serves as a vital barometer of the country’s economic activity, compliance health, and sectoral momentum. With India increasingly positioning itself as a global manufacturing hub, these figures are more than just data points—they’re indicators of policy success, investor sentiment, and national progress.
India’s Manufacturing Boom Pushes July GST Inflows
India’s manufacturing-powered GST surge in July 2025 is more than just a statistical win—it’s an economic signal. With ₹1.96 lakh crore in collections, a soaring PMI, robust state compliance, and strong import duties, India is showcasing resilience, industrial momentum, and digital tax governance. Professionals and businesses that stay tuned to these trends will find opportunities for smarter planning, better compliance, and stronger strategic positioning in both local and global markets.

| Metric | July 2025 Value | Year-on-Year Change |
|---|---|---|
| Gross GST Revenue | ₹1.96 lakh crore | +7.5% YoY |
| Net GST (post-refunds) | ₹1.69 lakh crore | +1.7% YoY |
| GST Refunds | ₹27,147 crore | +67% |
| Manufacturing PMI | 59.2 | 17-Year High |
| Manufacturing Output (June 2025) | +3.9% | — |
| Top Performing States | Punjab (+32%), AP (+12.1%) | State Revenue Increases |
| Official GST Website | gst.gov.in | — |
What Exactly Is GST and Why Should You Care?
For those new to GST, here’s the short and sweet version: GST (Goods and Services Tax) is a unified tax system introduced in 2017 that combines multiple indirect taxes into one. Every time you buy a product or service in India, a part of what you pay goes to GST. Businesses collect it, the government monitors it, and everyone benefits when the system works efficiently.
Increased GST inflows aren’t just good news for government coffers—they reflect:
- Higher consumption levels
- Active business transactions
- Stronger manufacturing output
- Better tax compliance
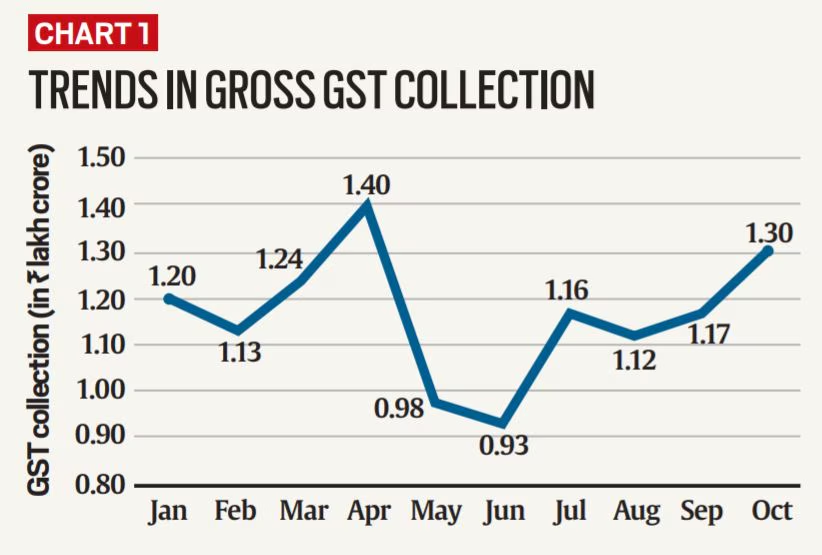
In July, India notched its seventh consecutive month of GST collections exceeding ₹1.8 lakh crore, proving the resilience of both consumer demand and supply chain performance.
India’s Manufacturing Boom Pushes July GST Inflows: PMI Hits 59.2
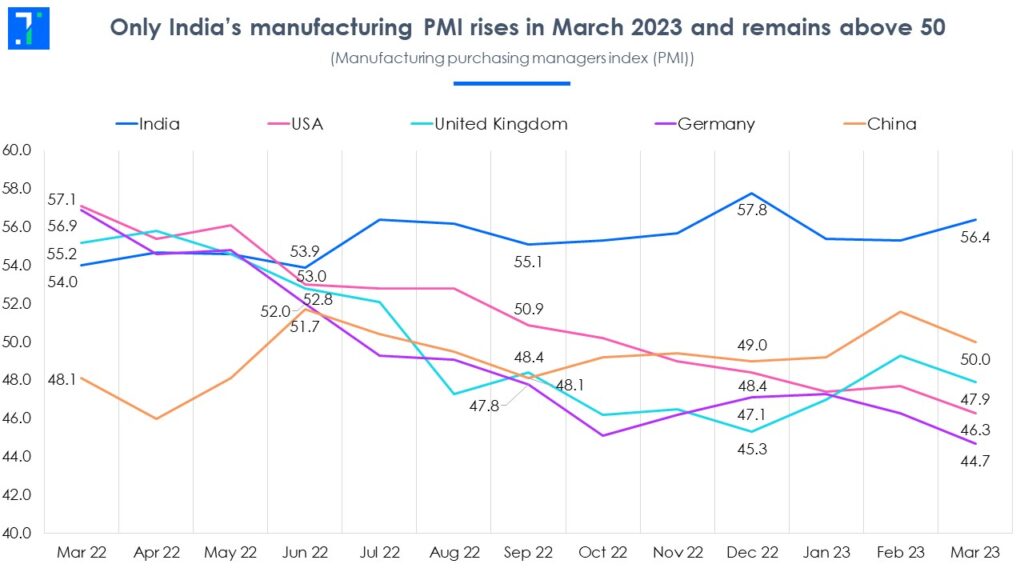
The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) for July climbed to 59.2, the highest since 2008. A PMI above 50 signals expansion, and when it inches closer to 60, economists interpret it as widespread sectoral growth.
This PMI surge was powered by:
- New domestic and international orders
- Lower input costs compared to Q1
- Accelerated capital expenditure by mid-sized manufacturers
Leading contributors to this boom include:
- Automobile manufacturers, who reported record order books
- Electronics and white goods producers leveraging seasonal demand
- FMCG brands scaling up inventories for festive seasons
This boom translates directly into more taxable transactions under GST.
GST Performance: Monthly Comparison
To put July’s collections in context, here’s how recent months stack up:
| Month | GST Collection (₹ lakh crore) | Growth YoY |
|---|---|---|
| April 2025 | ₹2.10 | +12.2% |
| May 2025 | ₹2.10 | +10.3% |
| June 2025 | ₹1.85 | +6.1% |
| July 2025 | ₹1.96 | +7.5% |
While April and May rode the wave of annual return filings, July’s bounce-back after a dip in June reinforces the overall upward trajectory.
Sector-Wise GST Contribution: Who’s Pulling the Weight?
GST is collected at multiple stages—manufacturing, retail, services, and imports. Here’s a quick look at who contributed most:
Manufacturing Sector
Responsible for a lion’s share of the surge. Sub-segments such as auto, steel, electronics, and pharma saw higher outputs and input procurement.
Retail and FMCG
High-volume B2C sales attracted strong GST inflows. As rural markets revived post-monsoon, FMCG brands saw their supply chains heat up.
Imports
Import-related GST (IGST) collection rose 9.7% YoY, higher than domestic GST (6.7%). India imported more machinery, semiconductors, and industrial equipment—signaling long-term production investments.
Logistics and Warehousing
With more goods being manufactured and shipped, the logistics sector also reported an increase in taxable services, adding to GST.
State-Wise Analysis: Who’s Winning at Compliance?
Punjab: +32% GST Growth
A phenomenal performance attributed to:
- AI-based fraud detection
- Cancellation of fake GST registrations
- Departmental audits and geotagging of business locations
Punjab’s Finance Minister Harpal Singh Cheema credited “data transparency and accountability” as key drivers.
Andhra Pradesh: +12.1%
The state collected ₹3,803 crore in July, a record for the region. Advanced analytics and compliance incentives helped broaden the tax base.
Other Strong Performers
- Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu continued to top the absolute collection charts due to industrial bases and high urban consumption.
- Smaller states like Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand saw gains from eco-tourism and seasonal trade.
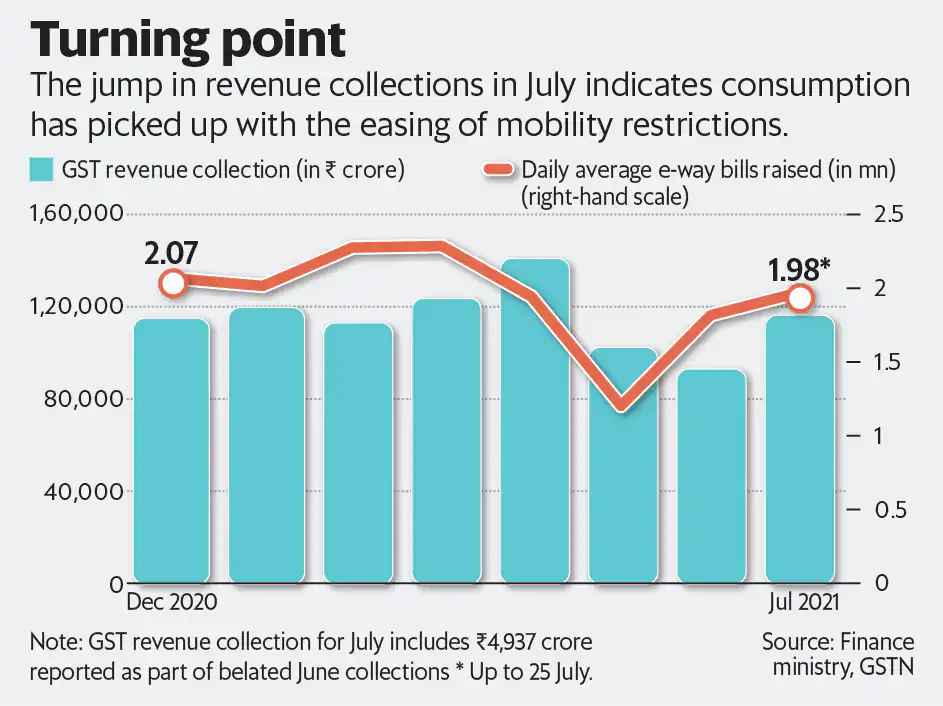
Refunds: A Sign of Business Maturity
July 2025 also witnessed ₹27,147 crore in GST refunds, a staggering 67% rise YoY.
Refunds are typically claimed by:
- Exporters (zero-rated supplies)
- Manufacturers with input tax accumulation
- SEZ units and businesses under inverted duty structures
This spike shows businesses are getting more tax savvy, keeping better books, and following the digital trail.
GST and the Global Investor Lens
International investors watch GST collections as a sign of:
- Market stability
- Consumption resilience
- Manufacturing efficiency
India’s PLI (Production-Linked Incentive) schemes, low-cost labor, and robust digital taxation framework have made it a darling for foreign direct investment (FDI) in sectors like mobile phones, electric vehicles, and green energy.
According to data from DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade), India attracted over $50 billion in FDI in FY 2024–25, much of it concentrated in manufacturing-heavy states.
Practical Takeaways for Business Owners and Professionals
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, tax consultant, or corporate strategist, July’s GST data provides some valuable cues:
- File Early: With stricter timelines and e-invoicing mandates, early filing avoids interest penalties and audit flags.
- Claim Refunds: Ensure accurate matching of GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B to streamline refund claims.
- Watch Sector Trends: Know your industry’s tax patterns. Manufacturing is seeing high scrutiny for input/output mismatches.
- Stay Updated: Track policy changes via CBIC’s GST Portal and the GSTN Help Center.
Step-by-Step Guide: How GST Growth Happens
- Raw Materials Purchased → Tax Paid on Inputs
- Production & Sales → GST Collected from Buyers
- GST Filed → Monthly returns submitted on portal
- Refunds & Credits → Eligible claims processed
- Government Allocation → Revenue split between Centre & States
This cycle repeats across millions of transactions daily, and higher volumes mean stronger GST flows.
Policy Support: How the Government Helps Fuel Growth
The Indian government has actively supported GST performance through:
- Mandatory e-invoicing for businesses with turnover above ₹5 crore
- AI-powered GSTN analytics to flag discrepancies
- Real-time GSTR-2B matching for input credits
- Linking of Aadhaar with GSTIN to prevent fraud
Such measures have made India’s tax system one of the most transparent and efficient in the developing world.
Telangana High Court Delivers Major Relief for NRSC in GST Dispute
GST Portal to Be Down August 2–3 — Check Exact Hours Before Filing
Groundbreaking High Court Ruling on GST and Expat Employee Secondments—What It Means for Businesses!










