ITR Filing FY 2024-25: Filing your taxes isn’t just a legal duty—it’s your power move as a financially responsible citizen. For the Financial Year (FY) 2024-25, which corresponds to the Assessment Year (AY) 2025-26, having your ducks in a row (or rather, your documents) is the difference between smooth sailing and a frustrating audit letter. Whether you’re a first-time filer or a seasoned tax pro, “ITR Filing FY 2024-25: 8 Must-Have Documents for AY 2025-26” is your ultimate checklist. In this guide, we break down everything you need to file your Income Tax Return (ITR) accurately and confidently. Let’s dig in.
ITR Filing FY 2024-25
Filing your Income Tax Return for FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26) is easier when you have a complete document checklist. Whether you’re earning a monthly salary, running a business, investing in mutual funds, or mining Ethereum, getting your paperwork sorted is your first step. Start early, verify your details, and use the right tools. Tax season doesn’t have to be stressful—especially when you’re informed and prepared.

| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| ITR Filing Period | For FY 2024-25 (AY 2025-26), due date extended to Sept 15, 2025 for non-audit cases. |
| Must-Have Docs | Form 16, 26AS, AIS, capital gains, interest certs, foreign income, tax-saving proof, PAN, Aadhaar |
| Best ITR Forms | ITR-1 for salaried; ITR-2/3 for capital gains/business income |
| Statutory Requirement | As per Income Tax Act, 1961 |
| Official Filing Site | https://www.incometax.gov.in |
| Penalty for Late Filing | Up to ₹5,000 under Section 234F |
| New Compliance Rules | Enhanced reporting for crypto, ESOPs, and foreign assets |
| Tools to Use | AIS-TIS sync tools, refund tracker, Excel/JSON utility |
Why Filing ITR Matters (and What Could Go Wrong)?
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) isn’t just a box to check—it’s a serious financial document that impacts your credibility. Here’s why:
- Want a loan, visa, or credit card? Lenders check your ITR.
- Planning to claim a tax refund? No ITR, no refund.
- Got foreign assets or crypto holdings? You’re legally required to report them.
- Received TDS deductions? You need to file ITR to claim your share.
- Avoid penalties and scrutiny under Income Tax Act Sections 234F, 139(9), and 143(1).
In short, skipping ITR can cost you more than just time.
The 8 Must-Have Documents for ITR Filing FY 2024-25
1. Form 16 – Your Salary Report Card
Issued by your employer, Form 16 summarizes your salary, tax deductions, and TDS paid. Think of it as your year-end paycheck summary.
Split into two parts:
- Part A: TDS details, employer TAN, PAN
- Part B: Salary breakup, deductions under Chapter VI-A
Make sure the PAN on your Form 16 is accurate. Any mismatch could lead to a processing delay.
Tip: Use Form 16 to pre-fill ITR forms for faster, error-free filing.
2. Form 26AS, AIS, and TIS – Your Digital Tax Footprint
- Form 26AS: Reflects tax deducted on your behalf (TDS), advance tax payments, and refund status.
- AIS (Annual Information Statement): Tracks all your financial transactions—interest, dividends, share trades, foreign remittances.
- TIS (Taxpayer Information Summary): Simplified summary of AIS data.
All are downloadable from TRACES or the official income tax portal.
Example: If your bank paid you ₹10,000 interest but it isn’t in AIS, the IT department could still flag it. Reconcile early.
3. Capital Gains Statement – If You Sold Stocks, Crypto, or Property
If you made capital gains from:
- Shares or mutual funds
- Real estate property
- Crypto or NFTs
…you must report it.
Short-term gains (assets held <12 months) are taxed as per your slab. Long-term gains (assets held >12 months) are taxed at 10% (above ₹1 lakh).
How to get it: Platforms like Zerodha, CoinSwitch, or CAMS offer year-end capital gains summaries.
4. Interest Certificates and Bank Statements
Banks and NBFCs issue interest certificates for:
- Savings accounts
- Fixed deposits (FDs)
- Recurring deposits (RDs)
These interests are taxable. Even if TDS wasn’t deducted, you still need to report the income.
Pro Tip: Log in to your net banking account and check the “Interest Summary” or “Tax Statement” tab to download the certificate.
5. Tax-Saving Investment Proof
To claim deductions under:
- Section 80C (₹1.5 lakh): ELSS, PPF, life insurance, tuition fees
- Section 80D: Health insurance premiums
- Section 80E: Interest on education loans
- Section 80G: Charitable donations
You must keep payment receipts, insurance certificates, or donation acknowledgments.
If you claim HRA (House Rent Allowance), retain:
- Rent receipts
- PAN of landlord (if rent > ₹1 lakh/year)
- Rental agreement
6. Foreign Income & Unlisted Shareholdings
Global income and foreign asset disclosures are a must if you:
- Work with international clients
- Own foreign stocks (e.g., through INDmoney, Vested)
- Hold money in foreign banks
Also required:
- Foreign ESOP disclosures
- Holdings in overseas crypto exchanges
Non-disclosure can attract fines under the Black Money Act, so declare them, even if there’s no income generated.
7. PAN and Aadhaar Card
- Both are mandatory for filing returns
- PAN-Aadhaar linking deadline: June 30, 2025
- Returns won’t process without linking
8. Bank Account Details
To receive your tax refund smoothly, you must:
- Provide valid bank account details
- Pre-validate account on income tax portal
- Ensure mobile number is linked to the bank for OTP-based e-verification
Add multiple accounts, but only one should be marked as primary.
What’s New for AY 2025-26?
1. Crypto Tax Compliance
You must report income from digital assets under Section 115BBH, even if you incurred losses. Gains are taxed at 30% flat, without deductions.
2. Mandatory ESOP Reporting
If you’ve been allotted ESOPs from a foreign employer, they must be reported even if not exercised.
3. Foreign Assets
Disclosure expanded to include:
- Foreign real estate
- Offshore trusts
- Retirement benefits (e.g., 401(k), IRA)
4. ITR Utilities Updated
Excel/JSON utilities now include:
- Pre-filled capital gain fields
- AI-based validation
- Schedule-specific flagging for errors
5. AIS-TIS Reconciliation Mandatory
Before submission, reconcile your numbers with AIS to avoid mismatches and Section 143(1) notices.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Your ITR
Step 1: Collect and Organize All Docs
Make a digital folder with the 8 must-have documents. Name them clearly (e.g., “Form16_Employer2025.pdf”).
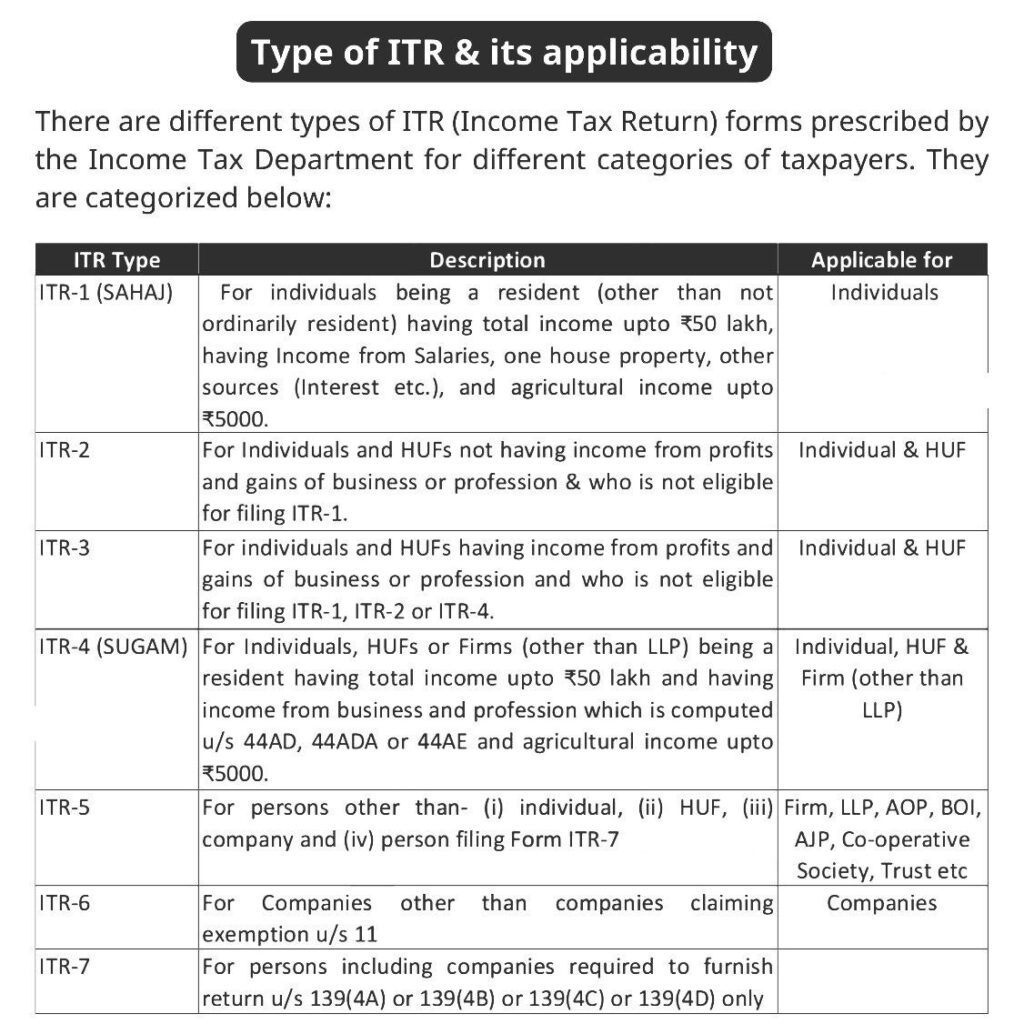
Step 2: Choose the Correct ITR Form
| Income Type | Suggested ITR Form |
|---|---|
| Salary Only (< ₹50L) | ITR-1 |
| Capital Gains | ITR-2 |
| Freelance/Business | ITR-3 |
| Presumptive Income | ITR-4 |
Step 3: Download the Latest Excel/JSON Utility
- Import pre-filled data using your PAN
- Match AIS and TIS fields
- Validate fields to ensure zero errors
Step 4: Submit Return
- Preview and cross-check all entries
- Submit and e-verify using Aadhaar OTP or Net Banking
Step 5: Track Refund Status
Track status using the ‘View Returns/Forms’ feature on the portal.
ITR Filing 2025 Warning: 7 Common Issues Taxpayers Must Watch Out For
Filing ITR This Year? – 4 Key Points Every Salaried Taxpayer Must Remember
ITR 2025 Filing Guide – Why Students and Unemployed Must Not Skip It










