Top 7 Countries With Zero Income Tax: If you’ve ever dreamed about keeping every single dollar you earn without cutting a check to Uncle Sam, then “Top 7 Countries With Zero Income Tax You Might Want to Move To” is a topic you’ll want to explore. Around the globe, a handful of nations have completely eliminated personal income tax. Sounds like a dream, right? For many expats, retirees, and digital nomads, it’s not just a dream—it’s their daily reality. But let’s be real for a second. Moving to a tax-free country isn’t as simple as showing up with a suitcase. These countries offer unique opportunities, but they also come with challenges—cost of living, residency requirements, and cultural adjustments. In this guide, we’ll break down the top seven tax-free countries, explain how they sustain themselves without income tax, and help you figure out whether relocating could actually work for you.
Top 7 Countries With Zero Income Tax
Living in a zero-income-tax country is a bold move that can transform your finances. But it’s not just about keeping more of your paycheck—it’s about matching your lifestyle with a new culture, navigating residency rules, and preparing for different costs. Whether you’re a digital nomad craving island life, a retiree looking to stretch your savings, or a high-net-worth individual seeking financial efficiency, there’s a tax-free destination for you. Just remember: the grass isn’t always greener—it’s just taxed differently.

| Feature | Data / Info | Source / Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Number of countries with zero income tax | About 20 globally | OECD |
| Top choices for expats | UAE, Monaco, Bahamas, St. Kitts & Nevis, Vanuatu, Antigua & Barbuda, Brunei | Investopedia |
| GDP (example) | UAE: $499B, Monaco: $7.2B, Bahamas: $14.9B | World Bank |
| Cost of living index | Monaco: 160+, UAE: 65, Bahamas: 84 | Numbeo |
| US expats note | U.S. citizens are taxed worldwide, even abroad | IRS |
| Residency/Citizenship pathways | Golden Visas, Citizenship by Investment, property ownership | Global Citizen Solutions |
Why Do Some Countries Have Zero Income Tax?
It might seem odd that some countries completely skip personal income tax. Historically, most countries adopted income tax during the 20th century, especially to fund wars and social programs. Yet, others chose different revenue models.
- Resource-rich states like the United Arab Emirates and Brunei bankroll their budgets with oil and gas revenues.
- Tourism-driven economies such as the Bahamas or Antigua rely heavily on foreign visitors, service industries, and investment inflows.
- Banking hubs like Monaco attract wealthy residents, boosting consumption and property markets instead of taxing wages.
- Indirect taxation in these nations comes in the form of VAT, duties, or higher costs for goods and services.
In short: while you won’t see a chunk of your salary going to income tax, you’ll likely pay more when you shop, import, or own property.
Top 7 Countries With Zero Income Tax
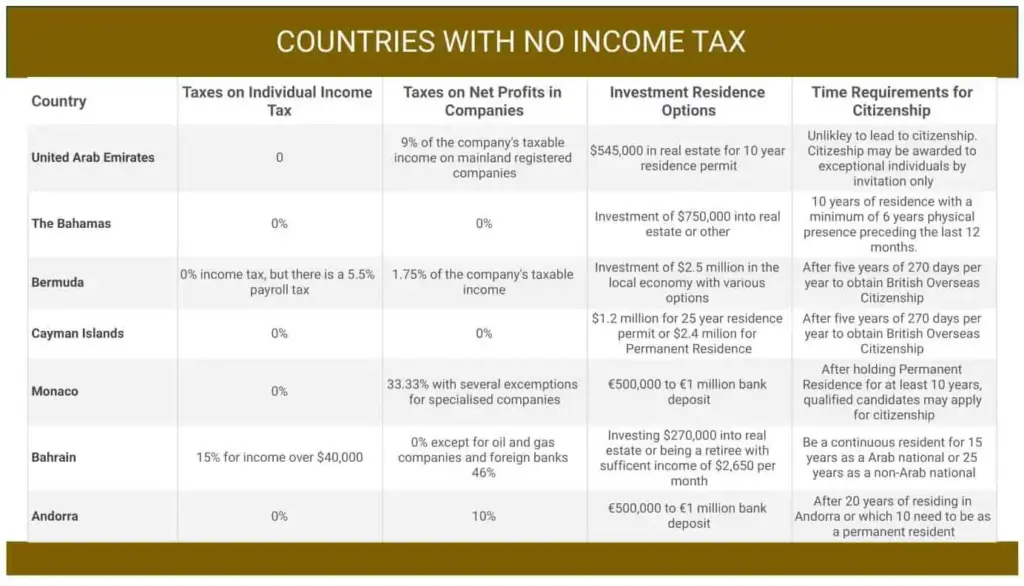
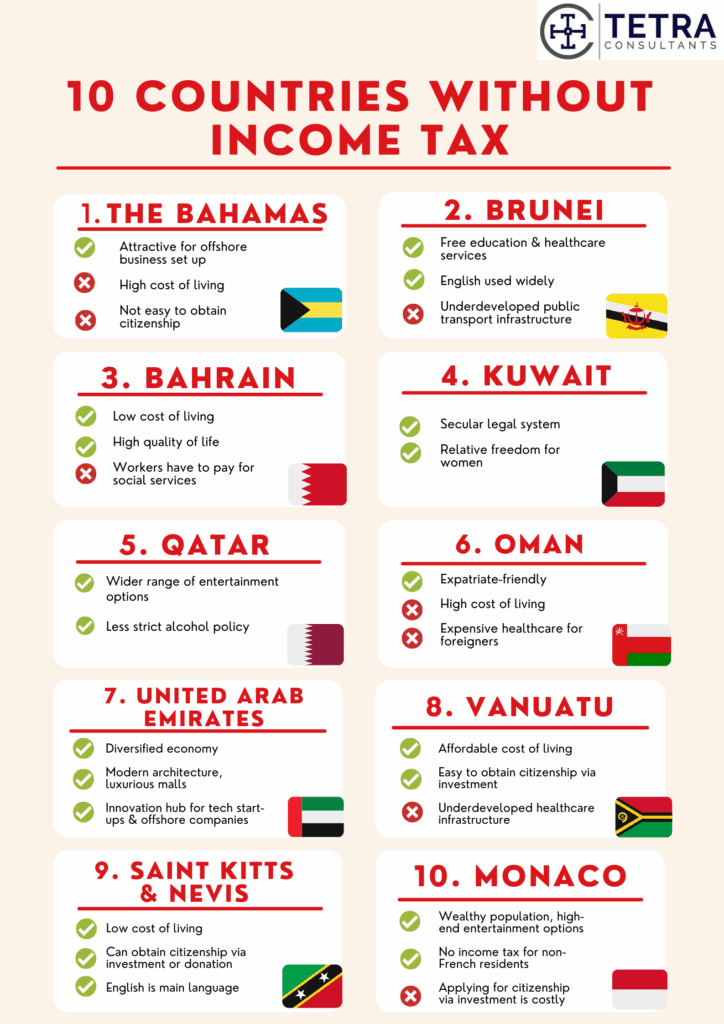
1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
- Why it’s attractive: Dubai and Abu Dhabi are already expat magnets, offering luxury lifestyles, tax-free salaries, and modern infrastructure.
- GDP: $499 billion (World Bank, 2023).
- Population: 9.5 million, with 80% expats.
- Residency: Golden Visas for investors, skilled professionals, and entrepreneurs.
- Lifestyle: World-class healthcare and international schools, though both come at a price.
- Catch: Cost of living is high—rent in Dubai averages $2,000–$3,000 a month for central apartments.
2. Monaco
- Why it’s attractive: Known as the playground of the rich, Monaco has had no personal income tax since the 1800s.
- GDP per capita: Roughly $190,000—one of the highest worldwide.
- Residency: Requires substantial proof of wealth and at least €500,000 in a local bank account.
- Lifestyle: Safe, glamorous, and positioned in the heart of Europe.
- Catch: Real estate is notoriously expensive, with apartments often costing millions.
3. The Bahamas
- Why it’s attractive: No income, inheritance, or capital gains taxes. Proximity to the U.S. makes it especially popular with American retirees.
- GDP: $14.9 billion.
- Residency: Permanent residency often linked to real estate purchases ($750,000+ property).
- Lifestyle: Relaxed Caribbean vibe, English-speaking, and stunning beaches.
- Catch: Imported goods cost 30–40% more than in the U.S. Healthcare is improving but can be limited compared to larger countries.
4. St. Kitts and Nevis
- Why it’s attractive: This twin-island nation pioneered the Citizenship by Investment program in 1984.
- Population: About 54,000.
- Residency: Citizenship through a $150,000 donation or $200,000+ in real estate.
- Lifestyle: Peaceful, small-community living with strong ties to tourism.
- Catch: Limited job opportunities unless you’re self-employed or remote-working.
5. Vanuatu
- Why it’s attractive: No income tax, plus one of the fastest citizenship programs (as little as 60 days).
- Population: Around 300,000.
- Residency: Citizenship by donation (~$130,000).
- Lifestyle: Tropical and laid-back, though infrastructure is less developed.
- Catch: Geographic isolation makes international travel difficult.
6. Antigua and Barbuda
- Why it’s attractive: No personal income tax, no capital gains tax, and English as the official language.
- Residency: Citizenship by Investment starts at $100,000 donation.
- Lifestyle: Known for sailing, tourism, and a strong sense of community.
- Catch: Hurricanes and natural disasters can impact long-term living.
7. Brunei
- Why it’s attractive: Backed by oil wealth, Brunei has no personal income tax. Residents benefit from subsidized healthcare and education.
- GDP per capita: About $37,000.
- Residency: Hard for outsiders to secure long-term residency unless tied to employment in oil, gas, or government.
- Lifestyle: Safe, conservative, and structured, but limited entertainment options.
- Catch: Cultural adjustment may be challenging for some expats.
Living Tax-Free: The Real Costs
Living in these nations might free up your income, but you’ll face trade-offs:
- Higher property and rent prices in places like Monaco and UAE.
- Healthcare limitations in smaller islands like St. Kitts or Vanuatu.
- Education expenses—international schools in Dubai or Monaco can run $20,000–$40,000 a year.
- Social adaptation—life in Brunei or Vanuatu is drastically different from the fast-paced U.S.
Zero Tax vs. Low Tax Countries
Sometimes, low-tax countries can be more practical.
- Singapore: Taxes range from 0–22%, but it’s a global business hub with world-class infrastructure.
- Switzerland: Tax rates of 11–24%, with unmatched banking stability.
- Ireland: 20–40%, but it’s a hotspot for tech companies and startups.
In many cases, low-tax nations offer broader career opportunities while still providing significant tax advantages.
Checklist: Before Moving Abroad
- Check residency rules – Each country has unique pathways.
- Understand U.S. tax law – The IRS taxes worldwide income unless you renounce citizenship.
- Calculate cost of living – Use resources like Numbeo.
- Plan for healthcare – International health insurance is often necessary.
- Look into education – Factor in schooling if moving with kids.
- Consult professionals – Tax advisors and immigration lawyers are essential.
Big Tax Bill Update – Child Tax Credit Changes Every Family Should Know About
DGFT Expands GAEC Scope: New Amendments Include More Chemicals & Countries in HBP 2023
Whistleblower Punished? Pension Agency Suspends Manager After He Flags R21m Payment