US Abruptly Cancels India Trade Talks Amid Tariff Tensions: The US abruptly cancels India trade talks amid tariff tensions, and this sudden move is more than just a diplomatic hiccup. It’s a development with ripple effects across agriculture, technology, manufacturing, and global supply chains. Both countries—two of the world’s largest democracies—have been working for years to strengthen trade ties, but the latest standoff highlights how politics, tariffs, and power struggles can stall progress. Washington pulled out of the planned sixth round of trade talks, scheduled for August 25–29, 2025, in New Delhi. Just days before, the U.S. announced steep new tariffs of 25%, which will bring duties on some Indian goods to nearly 50% starting August 27. This escalation underscores long-standing disagreements over agriculture, energy, and market access—plus frustration over India’s discounted oil imports from Russia.
US Abruptly Cancels India Trade Talks Amid Tariff Tensions
The U.S. abruptly canceling India trade talks amid tariff tensions is more than a diplomatic spat—it’s a test of a critical economic partnership. With tariffs rising to 50%, farmers in Iowa, exporters in Mumbai, and shoppers in New York all feel the impact. This dispute isn’t just about trade. It’s about global power dynamics, supply chain resilience, and the future of U.S.–India relations. Businesses, professionals, and consumers must prepare for a rocky road ahead by diversifying, budgeting smartly, and staying informed.

| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Event | U.S. cancels India trade talks (August 2025) |
| Reason | Tariff escalation and India’s oil imports from Russia |
| New Tariffs | 25% hike on top of existing duties, raising some products to 50% |
| Top Goods Affected | Textiles, steel, agricultural imports, IT-linked services |
| India’s Response | Modi doubles down on self-reliance and farmer protections |
| Trade Volume | $200+ billion in goods & services (2023, U.S. Census Bureau) |
| Official Source | U.S. Trade Representative |
Why the Talks Collapsed?
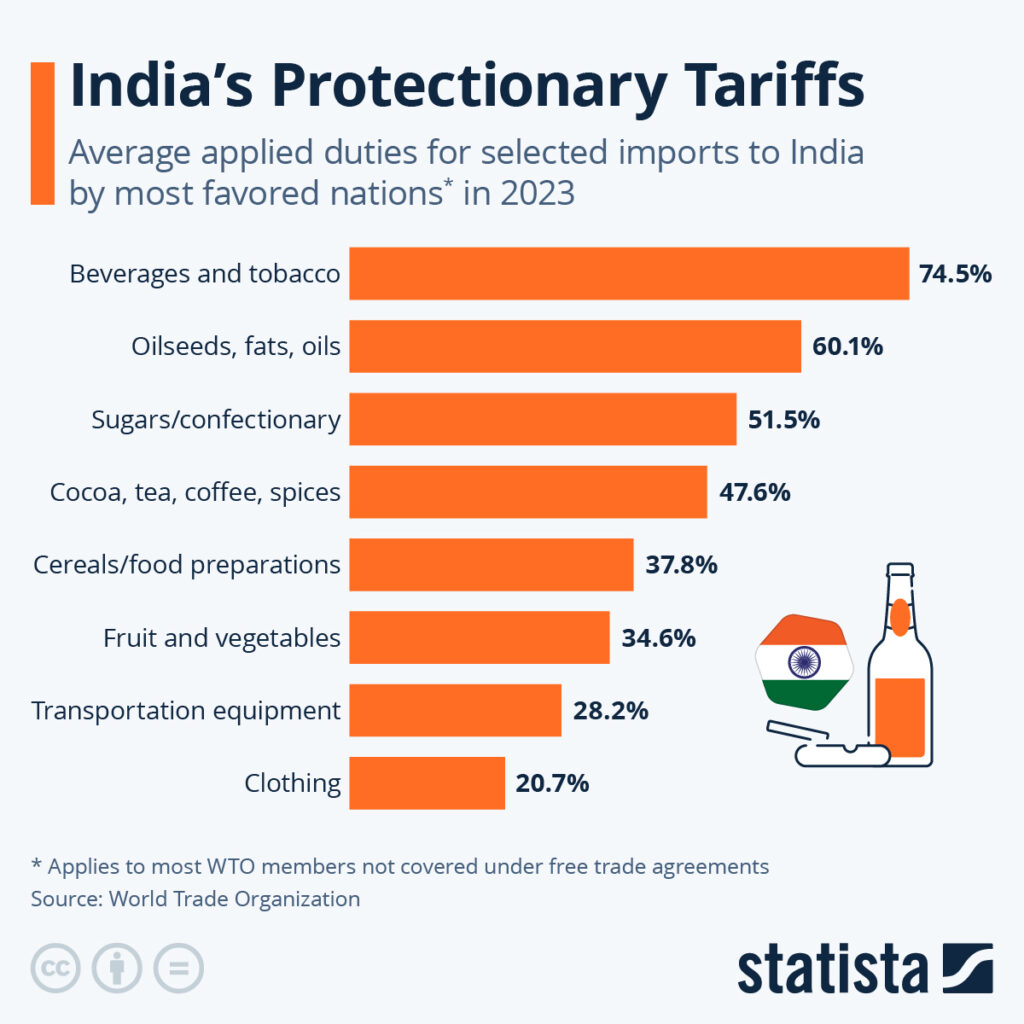
The U.S. has been pressing India for years to grant more access to its agriculture and dairy markets. American dairy producers, for instance, want India to reduce restrictions that keep out U.S. milk powder and cheese. But Prime Minister Narendra Modi has consistently argued that India’s farmers must be protected. On India’s Independence Day (August 15, 2025), he reinforced this stance, promising new protections and tax relief for rural producers.
Add in India’s ongoing purchases of Russian crude oil—which the U.S. views as undercutting its sanctions—and tensions boiled over. Washington decided it was better to walk away from the table than negotiate under those conditions.
What Tariffs Mean in Real Terms?
Tariffs aren’t just government jargon—they show up in your wallet and in business ledgers.
- For American Farmers: A 50% duty means fewer opportunities to export soybeans, dairy, and meat to India. Those lost sales hurt farm incomes in states like Iowa and Wisconsin.
- For Manufacturers: Indian exports of textiles, steel, and auto parts will cost more. U.S. companies may face supply chain disruptions.
- For Shoppers: Imported products like basmati rice, spices, or Indian-made apparel could get more expensive at stores like Costco or Walmart.
In plain English: tariffs act like a hidden tax. You don’t see them directly, but you pay for them in higher prices.
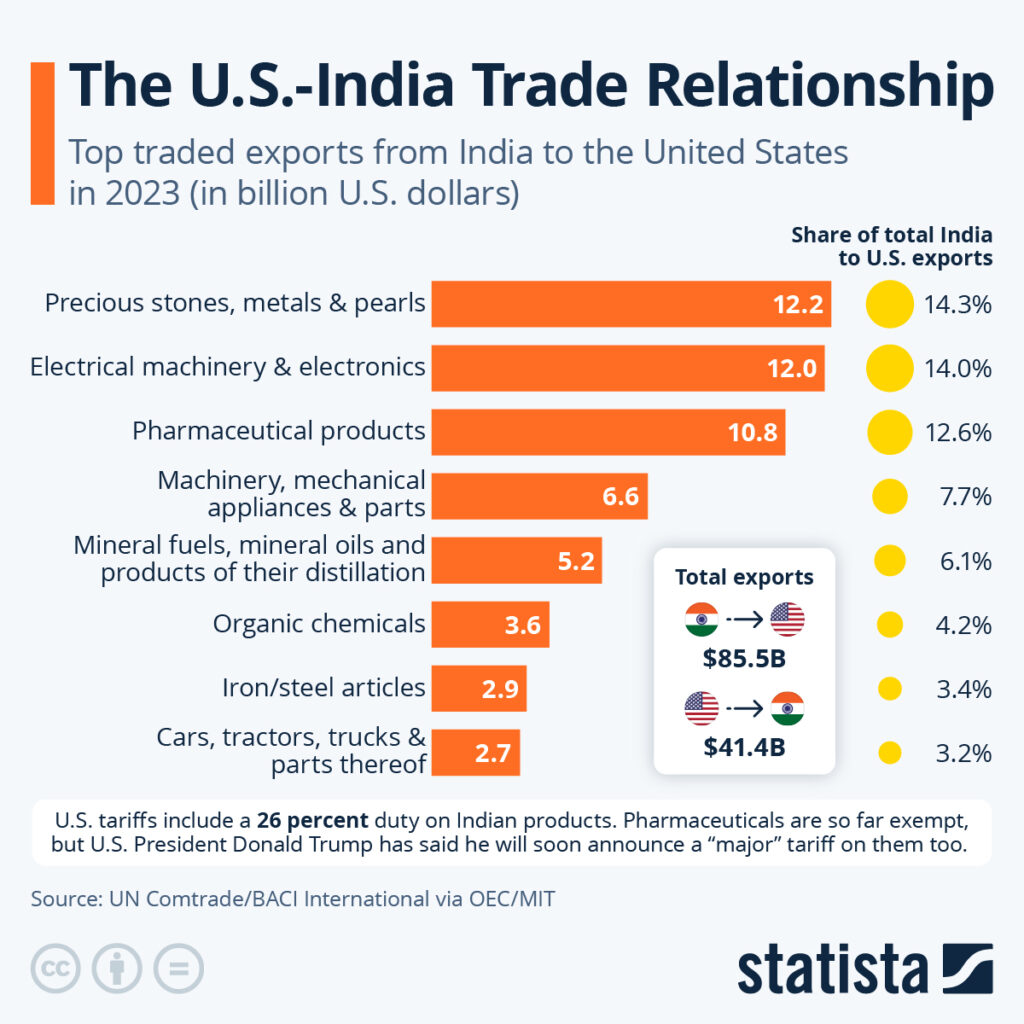
By the Numbers: U.S.–India Trade
According to the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative and the U.S. Census Bureau:
- U.S. goods exports to India (2023): $47.2 billion
- Top exports: oil, aircraft, farm products, machinery, medical instruments
- U.S. goods imports from India (2023): $97.4 billion
- Top imports: pharmaceuticals, textiles, steel, gems, jewelry, IT-related goods
- Services trade: India exports over $40 billion annually to the U.S. in IT and outsourcing
The U.S. runs a $50 billion trade deficit with India, which is one reason tariffs remain politically popular in Washington.
Historical Friction Points
This latest fallout is part of a long pattern:
- 2018: U.S. imposed tariffs on steel and aluminum, India responded with retaliatory tariffs.
- 2000s: Disputes over IT outsourcing and visa restrictions.
- Agriculture: Repeated fights over subsidies and dairy market access.
- Medical devices: India capped prices, frustrating U.S. manufacturers.
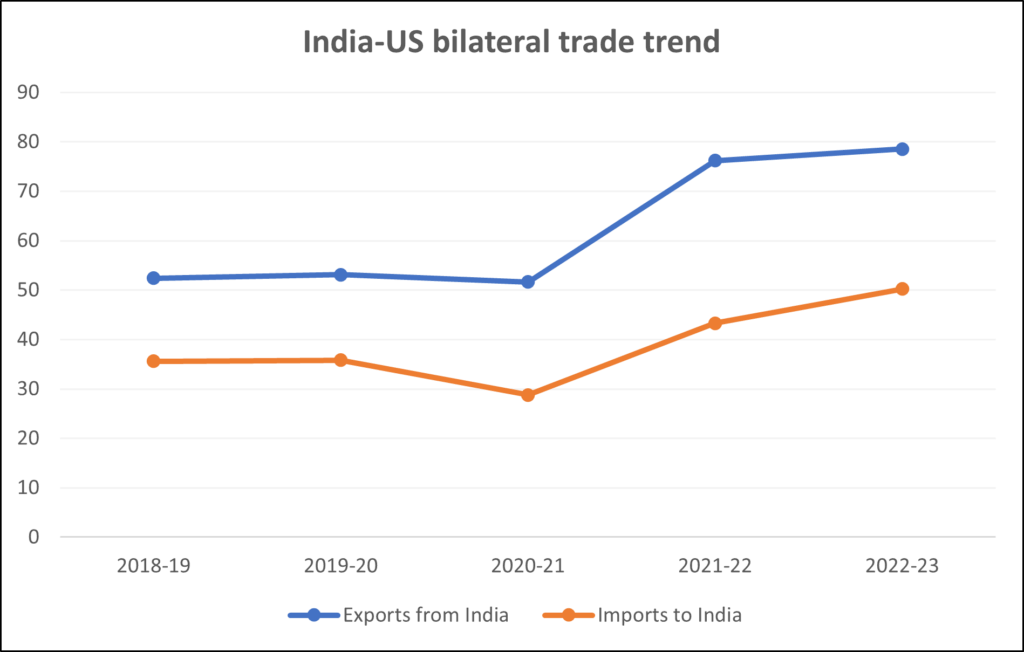
Yet despite the flare-ups, bilateral trade has continued to grow, making India a top 10 trading partner for the U.S.
India’s Self-Reliance Strategy
Modi’s answer to these challenges is Atmanirbhar Bharat—which translates to “self-reliant India.” His latest speech doubled down on:
- Tax incentives for local consumption
- Investment in domestic industries
- Farmer protections as both an economic and political priority
If tariffs escalate, India may look to expand trade with the EU, Japan, Southeast Asia, and deepen ties with Russia and China. This pivot could reduce U.S. influence in Asia and shift global trade patterns.
US Abruptly Cancels India Trade Talks Amid Tariff Tensions: Global Geopolitical Context
This standoff isn’t happening in a vacuum. The U.S. wants India as a strategic ally against China, but tariff disputes complicate that partnership.
- China remains America’s largest trading rival, with over $575 billion in bilateral trade.
- If India feels cornered, it may hedge its bets by aligning more closely with other powers.
- Energy plays a role too—India’s Russian oil imports keep its energy costs lower, giving it an economic advantage but fueling U.S. frustration.
In short, tariff tensions risk undermining the U.S.’s broader Indo-Pacific strategy.
Case Studies: Who Gets Hit
Dairy Industry: The National Milk Producers Federation has lobbied for years to expand access to India. Tariffs now make U.S. dairy exports even less competitive.
Textiles: India exports nearly $17 billion in textiles to the U.S. annually. Higher duties could hit small exporters in Indian hubs like Surat and Tiruppur.
IT Services: India’s IT giants—Infosys, TCS, Wipro—earn billions from U.S. contracts. If tariffs spill over into services, both sides lose.
Steel & Auto Parts: U.S. automakers sourcing Indian components may face higher costs, raising vehicle prices.
How Businesses Should Respond?
1. Map Supply Chains: Identify where you depend on Indian imports or U.S. exports to India.
2. Hedge Costs: Negotiate tariff-sharing clauses in contracts, or lock in rates now.
3. Diversify: Consider alternatives like Vietnam, Bangladesh, or Mexico.
4. Stay Informed: Monitor official sites such as USTR.gov and India’s Commerce Ministry.
5. Advocate: Trade associations like the U.S. Chamber of Commerce have historically secured tariff exemptions—make your voice heard.
Practical Advice for Consumers
- Expect higher prices: Imported rice, spices, and apparel may see hikes.
- Support local: Buying American-made can offset reliance on imports.
- Plan purchases: Retailers may absorb tariffs at first, but costs eventually pass to consumers.
Expert Perspectives
Trade experts warn that the collapse of talks sends the wrong signal at the wrong time. According to the Peterson Institute for International Economics, protectionist moves often backfire by shrinking export opportunities. Similarly, business groups like the U.S.-India Business Council argue that tariffs discourage investment and innovation in both countries.
Analysts also note that while tariffs may deliver short-term political wins, they rarely solve structural issues like market access or subsidies.
Timeline of U.S.–India Trade Tensions (2018–2025)
- 2018: U.S. imposes tariffs on steel/aluminum; India retaliates.
- 2020: Tensions over medical device price caps.
- 2022: Russia-Ukraine war pushes India to buy discounted oil, frustrating U.S.
- 2023: Trade crosses $200 billion, but disputes simmer.
- 2025: Sixth round of talks canceled; tariffs raised to 50%.
This timeline shows the cycle of growth and disputes that has defined the partnership.
Trump’s Tax Credit Shock Isn’t As Bad As Feared – Solar Stocks Surge Big
Maryland’s Digital Ad Tax Crushed – CCIA Scores Major Win
Infosys Hit With GST Fine In Singapore – What The Filing Reveals










